Obstructive symptoms
(Problems with the flow of urine)
- Difficulty starting urination
- Straining to urinate
- Incomplete bladder emptying
- Weak, slow, or intermittent urine stream
- Dribbling after urine.
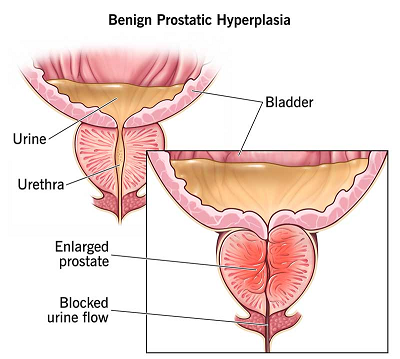
Benign prostatic hyperplasia :
Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), also referred to as benign prostatic hypertrophy, is diagnosed based on histology and is characterized by the proliferation of cellular elements within the prostate, leading to an enlarged prostate gland. Chronic bladder outlet obstruction (BOO) resulting from BPH can give rise to various complications such as urinary retention, impaired kidney function, recurrent urinary tract infections, gross hematuria, and the formation of bladder calculi. This condition typically manifests after the age of 50, often associated with hormonal changes in aging men, including an altered balance of hormones. Certain male hormones, such as dihydrotestosterone, are thought to exert a stronger influence on the prostate gland in later life.
The urethra — the tube that carries urine from the bladder to the outside of the body, passes directly through the prostate. Even a modest enlargement of the prostate can impede urination. As the bladder contends with the obstruction, its muscular walls may thicken, leading to issues such as increased frequency of bathroom visits and difficulties in fully emptying the bladder.
How Bothersome Is It ?
Physicians utilize either the International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS) or the American Urological Association symptom score to assess the frequency of a man’s symptoms related to benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). These are seven-item questionnaires focusing on typical BPH symptoms, providing a score ranging from 0 to 35.
Generally, men who score 8 and above are more inclined to consider their condition in need of treatment, although individual preferences vary. It’s important to note that there exists a spectrum of bother beyond a score of 8. Two men with the same symptom score may have different tolerances for their symptoms—one may tolerate it well, while the other may find it intolerable.
To add objectivity, both tests include an additional question: “If you were to spend the rest of your life with your urinary condition just the way it is now, how would you feel about that?” If the response is “I could live with it,” then postponing drug therapy or surgery might be a suitable approach for the individual.
A toolbox for managing Urinary symptoms :
BPH progresses slowly, so most men can decide for themselves if and when they would like to consider medication or surgery.
Medication use : Alter use of medications that could worsen urinary symptoms.
Consult with your doctor or pharmacist regarding prescription or over-the-counter medications that might be influencing your benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) symptoms. Certain medications, such as antihistamines and decongestants, may pose challenges for some individuals.
If you are taking medications that can increase urination, avoid taking them immediately before activities such as driving, traveling, attending events, or going to bed.
It is advised not to depend on ineffective dietary supplements. Despite their popularity, saw palmetto and other herbal supplements have not demonstrated efficacy in rigorous scientific testing so far.
Techniques :
There are several techniques and lifestyle changes you can try to relieve common urinary symptoms without relying on medication. However, if you’re experiencing persistent or severe symptoms, it’s important to consult a medical professional for proper diagnosis and guidance. Here are some techniques that may help:
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking enough water can help flush out toxins and maintain healthy urinary function. Aim for about 8 glasses (2 liters) of water per day, but adjust based on your activity level and individual needs.
- Bladder Training: If you have urinary frequency or urgency issues, bladder training can help. Gradually increase the time between bathroom visits, allowing your bladder to gradually hold more urine over time.
- Healthy Diet: Certain foods and drinks can irritate the bladder, worsening urinary symptoms. Limit or avoid caffeine, alcohol, acidic foods, and artificial sweeteners. Choose a well-rounded diet that includes an abundance of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Pelvic Floor Exercises: Strengthening your pelvic floor muscles can help improve urinary control and alleviate symptoms like urinary incontinence. Kegel exercises are a common way to target these muscles.
- Avoid Overstraining: Straining while urinating or having a bowel movement can weaken the pelvic floor muscles and exacerbate urinary symptoms. Take your time and avoid unnecessary straining.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Excess weight can put pressure on the bladder and worsen urinary symptoms. Maintaining a healthy weight through regular exercise and a balanced diet can help alleviate these issues.
- Avoid Smoking: Smoking can contribute to bladder irritation and increase the risk of urinary symptoms. Quitting smoking can have a positive impact on your overall urinary health.
- Limit Fluid Intake Before Bed: To reduce nighttime trips to the bathroom, try to limit your fluid intake in the hours leading up to bedtime.
- Manage Stress: Chronic stress can exacerbate urinary symptoms. Engage in relaxation techniques like deep breathing, meditation, or yoga to help manage stress.
- Toilet Habits: Ensure you fully empty your bladder when you urinate. Take your time on the toilet and avoid rushing. Leaning slightly forward and relaxing your pelvic muscles can help ensure thorough emptying.
- Avoid Constipation: Constipation can put pressure on the bladder and worsen urinary symptoms. Maintain regular bowel movements through a high-fiber diet and staying physically active.
- Scheduled Bathroom Breaks: If you’re experiencing frequent urgency, consider scheduling regular bathroom breaks to prevent sudden urges.
- Herbal Teas: Some herbal teas, like chamomile or marshmallow root tea, may have mild diuretic and anti-inflammatory properties that could potentially help with urinary discomfort.
Remember, these techniques might not work for everyone, and their effectiveness can vary depending on the underlying cause of your urinary symptoms. It’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and personalized advice. If your symptoms are severe or persistent, medical intervention may be necessary.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) ;
What is the most common urinary condition?
Common urinary symptoms include frequent urination, urgency (sudden and strong need to urinate), nocturia (waking up at night to urinate), urinary incontinence (involuntary leakage of urine), and difficulty starting or maintaining urination.
What is the most common cause of urinary?
Various factors can contribute to urinary symptoms, including urinary tract infections, overactive bladder, enlarged prostate (in men), pelvic floor dysfunction, hormonal changes, neurological conditions, and lifestyle factors such as dehydration or excessive caffeine intake.
How can I relieve urinary symptoms without medication?
There are several non-medical techniques that can help alleviate urinary symptoms, including behavioral changes, dietary adjustments, pelvic floor exercises, and lifestyle modifications.
What are some lifestyle modifications that can help?
Lifestyle changes such as maintaining a healthy weight, staying hydrated, avoiding bladder irritants (such as caffeine, alcohol, and acidic foods), and practicing good toilet habits (such as urinating regularly and fully emptying the bladder) can improve urinary symptoms.
What are pelvic floor exercises, and how do they help?
Pelvic floor exercises, also known as Kegel exercises, involve contracting and relaxing the muscles of the pelvic floor. These exercises can help strengthen the muscles that control urination, improving bladder control and reducing urinary leakage
Are there specific dietary changes I should make?
Certain dietary modifications, such as reducing intake of caffeine, alcohol, and spicy or acidic foods, and increasing consumption of fiber-rich foods and fluids, can help manage urinary symptoms by reducing bladder irritation and promoting healthy urinary function
Can stress management techniques help with urinary symptoms?
Yes, stress management techniques such as relaxation exercises, deep breathing, mindfulness meditation, and yoga can help reduce stress-related urinary symptoms by promoting relaxation and reducing muscle tension in the pelvic area.
How can I improve my bladder emptying?
Techniques such as double voiding (urinating twice during each bathroom visit), applying gentle pressure to the lower abdomen to facilitate bladder emptying, and adopting a relaxed sitting posture on the toilet can help improve bladder emptying and reduce residual urine volume.
How can I train my bladder to reduce urgency and frequency?
Bladder training techniques involve gradually increasing the intervals between urination, using distraction techniques to delay urination when feeling the urge, and practicing relaxation exercises to manage urgency and frequency.
What role does fluid intake play in managing urinary symptoms?
Proper hydration is important for maintaining healthy urinary function, but excessive fluid intake, especially before bedtime, can exacerbate nocturia (nighttime urination). Balancing fluid intake throughout the day and reducing intake before bedtime can help manage nocturia.
How long does it take to see improvement with these techniques?
The time it takes to see improvement varies depending on the individual and the severity of their symptoms. Consistent practice of behavioral and lifestyle techniques, along with patience and persistence, can lead to gradual improvement over time.
When should I consult a healthcare professional for urinary symptoms?
If urinary symptoms persist despite trying non-medication techniques, or if they are accompanied by pain, blood in the urine, recurrent urinary tract infections, or other concerning symptoms, it's important to consult a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and management.
|