Introduction :
A perianal abscess is a collection of pus that forms near the anus. It is a common condition that can be painful and uncomfortable. They occur when bacteria enter and multiply in the small glands and ducts in this area. If left untreated, perianal abscesses can lead to severe complications such as fistulas, which are abnormal connections between the anus and other organs. In this blog, we will discuss the causes, signs and symptoms, as well as the treatment and precautions for perianal abscesses.
Causes of Perianal Abscess :
- Blockage of an anal gland
- Infection of an anal fissure
- Sexually transmitted infection (STI)
- Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)
- Immunocompromised state
Signs and Symptoms :
- Pain and swelling around the anus
- Redness and warmth around the anus
- A lump or nodule near the anus
- Pus discharge from the anus
- Constipation or diarrhea
- Fever
Management :
- Medical Evaluation: If you suspect you have a perianal abscess, it’s essential to see a healthcare provider or a colorectal specialist. They will examine the abscess and may order imaging tests, such as an ultrasound or MRI, to determine the extent and location of the infection.
- Incision and Drainage (I&D): The primary treatment for a perianal abscess is surgical drainage. This procedure is typically performed in a doctor’s office or an operating room, depending on the abscess’s size and location. The steps include:a. Local Anesthesia : The area around the abscess is numbed with a local anesthetic to minimize pain during the procedure.b. Incision: A small incision is made in the abscess to allow the pus to drain out. Sometimes, a larger incision may be required for deeper abscesses.c. Drain Placement: A drain may be placed inside the wound to keep it open, allowing for continued drainage and preventing the abscess from re-forming.
- Antibiotics: In some cases, your healthcare provider may prescribe antibiotics before or after the drainage procedure, especially if there is a risk of the infection spreading or if the abscess is associated with a more extensive infection.
- Pain Management: Over-the-counter or prescription pain relievers may be prescribed to manage pain and discomfort following the procedure.
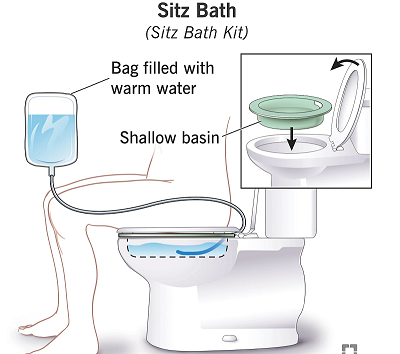
- Warm Sitz Baths: Soaking in warm sitz baths can help promote healing and relieve discomfort. This involves sitting in a shallow, warm water bath for 15-20 minutes several times a day.
- Follow-up: It’s crucial to follow your healthcare provider’s instructions for wound care and attend all follow-up appointments. This ensures that the abscess heals properly and doesn’t reoccur.
- Lifestyle and Hygiene: Maintaining good perianal hygiene is essential to prevent future abscesses. This includes proper cleaning and avoiding excessive wiping after bowel movements. Some individuals with recurring abscesses may need to make dietary and lifestyle changes.
It’s important not to attempt to treat a perianal abscess at home. Surgical drainage by a healthcare professional is the most effective way to manage this condition and prevent complications such as fistulas or the spread of infection.
Precautions to take with perianal abscess
-
Maintain Good Hygiene :
Properly clean the anal area after bowel movements using mild, unscented soap and water. Gently pat the area dry instead of rubbing.
-
Avoid Over-Wiping :
Be gentle when wiping to avoid irritating the perianal region. Consider using wet wipes or a bidet for a more gentle cleaning process.
-
Fiber-Rich Diet :
Consume a high-fiber diet to prevent constipation, as straining during bowel movements can contribute to abscess formation. Fiber helps keep stools soft and regular.
-
Stay Hydrated :
Drink plenty of water to maintain adequate hydration and facilitate healthy bowel movements.
-
Practice Safe Sex :
Engaging in safe sexual practices can help prevent sexually transmitted infections (STIs) that could lead to perianal abscesses.
-
Avoid Anal Trauma :
Take precautions during activities that might lead to trauma or injury to the perianal area, such as rough anal intercourse.
-
Prompt Treatment of Anal Fissures :
If you have anal fissures (small tears in the anal lining), seek treatment promptly to prevent infection and the potential development of an abscess.
-
Manage Diabetes :
If you have diabetes, keeping your blood sugar levels under control can reduce your risk of infections, including perianal abscesses.
-
Regular Exercise :
Engage in regular physical activity to promote overall health and reduce the risk of conditions that may contribute to abscesses, such as obesity.
-
Avoid Tight Clothing :
Wearing tight-fitting clothing, especially around the waist and buttocks, can increase friction and irritation in the perianal area. Choose comfortable, loose-fitting attire.
Remember that while these precautions can help reduce the risk of perianal abscesses, they may not guarantee complete prevention.
Conclusion
If you suspect you have a perianal abscess or are experiencing symptoms like severe pain, swelling, redness, or fever, seek medical attention promptly. Early diagnosis and treatment are key to a successful recovery and the prevention of complications.
Additional information
- Perianal abscesses are more common in men than women.
- Perianal abscesses are more common in people with diabetes or other chronic health conditions.
- Perianal abscesses can sometimes lead to anal fistulas.