- Chest pain, especially with physical exertion
- Shortness of breath, especially with physical exertion
- Fatigue
- Arrhythmias (abnormal heart rhythms)
- Dizziness
- Lightheadedness
- Fainting (syncope)
- Swelling in the ankles, feet, legs, abdomen.
Associations ;
HCM progresses to other health problems ;
Atrial fibrillation ; This can lead to blood clots, stroke and other heart-related complications.
Sudden cardiac Arrest and Sudden cardiac death ; Sudden cardiac arrest and sudden cardiac death refer to the abrupt cessation of heart function triggered by an excessively rapid heartbeat, specifically ventricular tachycardia. In such instances, immediate emergency interventions, such as CPR and defibrillation, are crucial once symptoms manifest. Without timely administration of these treatments, the outcome can escalate to sudden cardiac death.
However, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is the most common cause of sudden cardiac death in people under age 35 especially in young athletes .
Heart Failure ; If you have heart failure, It means your heart doesn’t pump as well as it should. Symptoms of heart failure include:
- Difficulty breathing (shortness of breath).
- Feeling tired (fatigue) when you’re active.
- Swelling in your ankles, legs and abdomen.
- Need to urinate while resting at night.
- Dizziness, confusion, difficulty concentrating, fainting.
- Feeling that your heart is pumping too fast (palpitations).
- A dry, hacking cough.
- A full (bloated) , loss of appetite, or upset stomach.
Diagnosis ;
- Electrocardiogram (ECG) to detect abnormal heart rhythms.
- Stress tests to observe heart function during exercise.
- Cardiac MRI for detailed images of the heart’s structure.
- Genetic testing to identify mutations in relevant genes.
Treatment ;
Lifestyle modifications: Avoiding excessive physical exertion and dehydration.
Medications to manage symptoms and improve heart function:
- Beta-blockers are prescribed to decrease heart rate and alleviate strain on the heart.
- Calcium channel blockers are used to induce relaxation and dilation of blood vessels.
- diuretics are medications aimed at promoting the removal of excess fluid from the body.
- Anti-arrhythmic drugs to control irregular heartbeats.
May improve symptoms and function ,
- Myosin Inhibitor like Mavacamten
Surgical Procedures ;
Various surgical and nonsurgical interventions can be employed for the treatment of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM):
- Septal Myectomy; One such procedure is septal myectomy, also known as septal reduction therapy. This involves open-heart surgery and the surgical excision of a portion of the thickened heart muscle. .
- Alcohol Septal Ablation; Also called nonsurgical septal reduction therapy, Injecting alcohol into a specific artery to reduce the thickened muscle.
- Cardiac implantable electronic devices (CIEDs) ; It encompass various types of implants aimed at improving heart function., including:
- Implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD) – An ICD helps regulate a normal heartbeat by delivering an electric shock in response to the detection of an irregular heartbeat, thereby reducing the risk of sudden cardiac death .
- Pacemaker – Its a small devices that utilize electrical pulses to stimulate the heart to beat at a normal rate, are employed for individuals with a heart rate that is excessively slow.
- Cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) device – This device coordinates contractions between the heart’s left and right ventricles.
- Heart Transplant
Is it safe to get Pregnant if I have Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM)?
While pregnant individuals with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy may require specialized care, such as echocardiography, the majority can successfully navigate pregnancy and opt for a vaginal delivery. If you are contemplating pregnancy, it is essential to engage in discussions with your healthcare provider to assess associated risks. Your healthcare provider can provide guidance on the specific medications for hypertrophic cardiomyopathy that are safe to continue during pregnancy..
Prognosis ;
.
Conclusion ;
HOCM is a serious condition, but it can be managed with treatment. With proper care, most people with HOCM can live a normal life.
Here are some additional tips for managing HOCM:
Get regular exercise: Engaging in regular exercise can play a crucial role in strengthening the heart and enhancing its pumping function. .
Lose weight: Individuals who are overweight or obese, shedding excess weight can contribute to reducing the strain on the heart. .
Avoid caffeine and alcohol: Caffeine and alcohol can worsen the symptoms of HOCM.
Quit smoking: Smoking can damage the heart muscle and worsen the symptoms of HOCM.
Get regular checkups: Regular visits to your health care provider are essential to monitor your condition and make necessary adjustments to your treatment plan.
If you have any concerns about HOCM, please talk to your doctor.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) ;
What is hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM)?
HCM is a genetic heart condition where the heart muscle becomes abnormally thick (hypertrophied), making it harder for the heart to pump blood effectively.
What causes hypertrophic cardiomyopathy?
HCM is primarily caused by genetic mutations that affect the proteins responsible for muscle growth in the heart. It can be inherited from a parent with the condition.
What are the symptoms of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy?
Symptoms can vary widely and may include shortness of breath, chest pain, fatigue, palpitations (rapid or irregular heartbeat), fainting, or dizziness.
How is hypertrophic cardiomyopathy diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically involves a combination of medical history review, physical examination, imaging tests (such as echocardiogram), and genetic testing.
Is hypertrophic cardiomyopathy treatable?
While there is no cure for HCM, treatment aims to manage symptoms and prevent complications. This may include medications to improve heart function, lifestyle modifications, and in some cases, surgical procedures such as septal myectomy or alcohol septal ablation.
Can hypertrophic cardiomyopathy be prevented?
Since HCM is primarily genetic, it cannot be prevented entirely. However, genetic testing and counseling may be recommended for individuals with a family history of the condition.
What is the prognosis for individuals with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy?
The prognosis varies depending on the severity of symptoms and the presence of complications. With appropriate management, many individuals with HCM can lead relatively normal lives. However, in some cases, HCM can lead to serious complications such as heart failure, arrhythmias, or sudden cardiac death.
Are there any lifestyle restrictions for individuals with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy?
Depending on the severity of the condition and symptoms, doctors may recommend certain lifestyle modifications such as avoiding strenuous exercise or competitive sports, limiting alcohol intake, and maintaining a healthy weight.
Should family members of someone with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy be tested?
Family members of individuals with HCM may be at risk of inheriting the condition and may benefit from genetic testing and counseling to assess their risk.
What should I do if I suspect I or a loved one has hypertrophic cardiomyopathy?
If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms suggestive of HCM, it's important to seek medical evaluation promptly. A healthcare provider can perform appropriate tests and recommend a treatment plan tailored to individual needs.
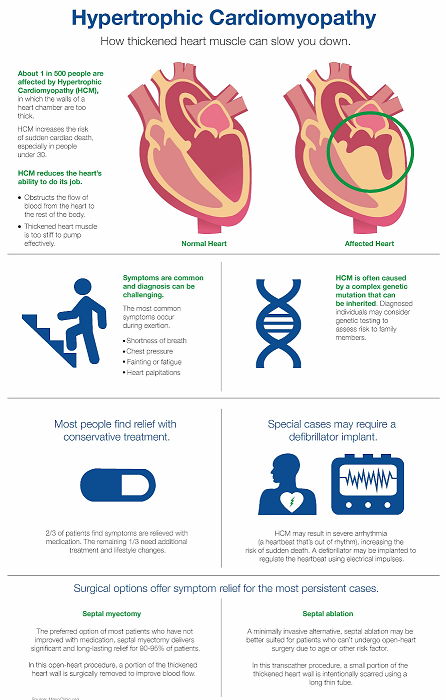
Hypertrophic Obstructive Cardiomyopathy (HCM) is a complex cardiac condition characterized by the thickening of the heart’s muscle wall, primarily affecting the left ventricle, left ventricle stiffness, Mitral valve changes and cellular changes. This condition can hinder the heart’s ability to pump blood efficiently and might lead to various symptoms and complications.
Incidence ;
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy affects an estimated 600,000 to 1.5 million Americans or 1 in 500 people. It is more prevalent than multiple sclerosis, a condition that impacts approximately 1 in 700 individuals.
Causes ;
The exact cause of HCM is unknown, but there are a number of factors that may contribute to the development of the condition, including:
- Genetic mutations proteins in the heart muscle are affected.
- Autosomal dominant inheritance pattern.
- Mutations in genes encoding sarcomere proteins.
- High blood pressure.
- Aging
- Often a familial condition, but sporadic cases can also occur.
Symptoms ;
Signs and symptoms of HCM include:
- Chest pain, especially with physical exertion
- Shortness of breath, especially with physical exertion
- Fatigue
- Arrhythmias (abnormal heart rhythms)
- Dizziness
- Lightheadedness
- Fainting (syncope)
- Swelling in the ankles, feet, legs, abdomen.

Associations ;
HCM progresses to other health problems ;
Atrial fibrillation ; This can lead to blood clots, stroke and other heart-related complications.
Sudden cardiac Arrest and Sudden cardiac death ; Sudden cardiac arrest and sudden cardiac death refer to the abrupt cessation of heart function triggered by an excessively rapid heartbeat, specifically ventricular tachycardia. In such instances, immediate emergency interventions, such as CPR and defibrillation, are crucial once symptoms manifest. Without timely administration of these treatments, the outcome can escalate to sudden cardiac death.
However, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is the most common cause of sudden cardiac death in people under age 35 especially in young athletes .
Heart Failure ; If you have heart failure, It means your heart doesn’t pump as well as it should. Symptoms of heart failure include:
- Difficulty breathing (shortness of breath).
- Feeling tired (fatigue) when you’re active.
- Swelling in your ankles, legs and abdomen.
- Need to urinate while resting at night.
- Dizziness, confusion, difficulty concentrating, fainting.
- Feeling that your heart is pumping too fast (palpitations).
- A dry, hacking cough.
- A full (bloated) , loss of appetite, or upset stomach.
Diagnosis ;
- Electrocardiogram (ECG) to detect abnormal heart rhythms.
- Stress tests to observe heart function during exercise.
- Cardiac MRI for detailed images of the heart’s structure.
- Genetic testing to identify mutations in relevant genes.
Treatment ;
Lifestyle modifications: Avoiding excessive physical exertion and dehydration.
Medications to manage symptoms and improve heart function:
- Beta-blockers are prescribed to decrease heart rate and alleviate strain on the heart.
- Calcium channel blockers are used to induce relaxation and dilation of blood vessels.
- diuretics are medications aimed at promoting the removal of excess fluid from the body.
- Anti-arrhythmic drugs to control irregular heartbeats.
May improve symptoms and function ,
- Myosin Inhibitor like Mavacamten
Surgical Procedures ;
Various surgical and nonsurgical interventions can be employed for the treatment of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM):
- Septal Myectomy; One such procedure is septal myectomy, also known as septal reduction therapy. This involves open-heart surgery and the surgical excision of a portion of the thickened heart muscle. .
- Alcohol Septal Ablation; Also called nonsurgical septal reduction therapy, Injecting alcohol into a specific artery to reduce the thickened muscle.
- Cardiac implantable electronic devices (CIEDs) ; It encompass various types of implants aimed at improving heart function., including:
- Implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD) – An ICD helps regulate a normal heartbeat by delivering an electric shock in response to the detection of an irregular heartbeat, thereby reducing the risk of sudden cardiac death .
- Pacemaker – Its a small devices that utilize electrical pulses to stimulate the heart to beat at a normal rate, are employed for individuals with a heart rate that is excessively slow.
- Cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) device – This device coordinates contractions between the heart’s left and right ventricles.
- Heart Transplant
Is it safe to get Pregnant if I have Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM)?
While pregnant individuals with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy may require specialized care, such as echocardiography, the majority can successfully navigate pregnancy and opt for a vaginal delivery. If you are contemplating pregnancy, it is essential to engage in discussions with your healthcare provider to assess associated risks. Your healthcare provider can provide guidance on the specific medications for hypertrophic cardiomyopathy that are safe to continue during pregnancy..
Prognosis ;
.
Conclusion ;
HOCM is a serious condition, but it can be managed with treatment. With proper care, most people with HOCM can live a normal life.
Here are some additional tips for managing HOCM:
Get regular exercise: Engaging in regular exercise can play a crucial role in strengthening the heart and enhancing its pumping function. .
Lose weight: Individuals who are overweight or obese, shedding excess weight can contribute to reducing the strain on the heart. .
Avoid caffeine and alcohol: Caffeine and alcohol can worsen the symptoms of HOCM.
Quit smoking: Smoking can damage the heart muscle and worsen the symptoms of HOCM.
Get regular checkups: Regular visits to your health care provider are essential to monitor your condition and make necessary adjustments to your treatment plan.
If you have any concerns about HOCM, please talk to your doctor.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) ;
What is hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM)?
HCM is a genetic heart condition where the heart muscle becomes abnormally thick (hypertrophied), making it harder for the heart to pump blood effectively.
What causes hypertrophic cardiomyopathy?
HCM is primarily caused by genetic mutations that affect the proteins responsible for muscle growth in the heart. It can be inherited from a parent with the condition.
What are the symptoms of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy?
Symptoms can vary widely and may include shortness of breath, chest pain, fatigue, palpitations (rapid or irregular heartbeat), fainting, or dizziness.
How is hypertrophic cardiomyopathy diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically involves a combination of medical history review, physical examination, imaging tests (such as echocardiogram), and genetic testing.
Is hypertrophic cardiomyopathy treatable?
While there is no cure for HCM, treatment aims to manage symptoms and prevent complications. This may include medications to improve heart function, lifestyle modifications, and in some cases, surgical procedures such as septal myectomy or alcohol septal ablation.
Can hypertrophic cardiomyopathy be prevented?
Since HCM is primarily genetic, it cannot be prevented entirely. However, genetic testing and counseling may be recommended for individuals with a family history of the condition.
What is the prognosis for individuals with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy?
The prognosis varies depending on the severity of symptoms and the presence of complications. With appropriate management, many individuals with HCM can lead relatively normal lives. However, in some cases, HCM can lead to serious complications such as heart failure, arrhythmias, or sudden cardiac death.
Are there any lifestyle restrictions for individuals with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy?
Depending on the severity of the condition and symptoms, doctors may recommend certain lifestyle modifications such as avoiding strenuous exercise or competitive sports, limiting alcohol intake, and maintaining a healthy weight.
Should family members of someone with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy be tested?
Family members of individuals with HCM may be at risk of inheriting the condition and may benefit from genetic testing and counseling to assess their risk.
What should I do if I suspect I or a loved one has hypertrophic cardiomyopathy?
If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms suggestive of HCM, it's important to seek medical evaluation promptly. A healthcare provider can perform appropriate tests and recommend a treatment plan tailored to individual needs.