Amenorrhea, the absence of menstrual periods, is a medical condition characterized by the lack of menstruation, defined as missing one or more menstrual cycles.
It is a normal occurrence in prepubertal, pregnant, and postmenopausal females. For women of reproductive age, the initial step in diagnosing no period is determining whether pregnancy is the cause.
In the absence of pregnancy, identifying the exact reason for absent menses becomes a challenge, causing concern and discomfort for those affected, impacting both physical and emotional well-being.
Menstruation :
- Hypothalamus : Controls the pituitary gland, which affects Ovulation ( releasing an egg).
- Ovaries : It secretes hormones estrogen and progesterone along with produce and store egg for ovulation.
- Uterus : Responds to the hormones by thickening the uterine lining. This lining sheds as menstrual period if there’s no pregnancy.
The menstrual cycle is an orderly progression of coordinated hormonal events that stimulates the growth of a follicle, that leading to the release of an egg and preparation of the uterine lining for implantation if fertilization occurs. If there’s no pregnancy that cycle, shed female uterine lining. That shedding is called period. There are many factors that can affect female period including issues with the following organs and structures:

Types of Amenorrhea:
Primary Amenorrhea: Primary amenorrhea occurs when a girl does not start her menstrual periods by the age of 16, in the presence of normal growth and secondary sexual characteristics. If by age 13 menses has not occurred and the onset of puberty, such as breast development, is absent, your healthcare provider should start workup . Common causes include genetic factors, anatomical abnormalities, and hormonal imbalances.
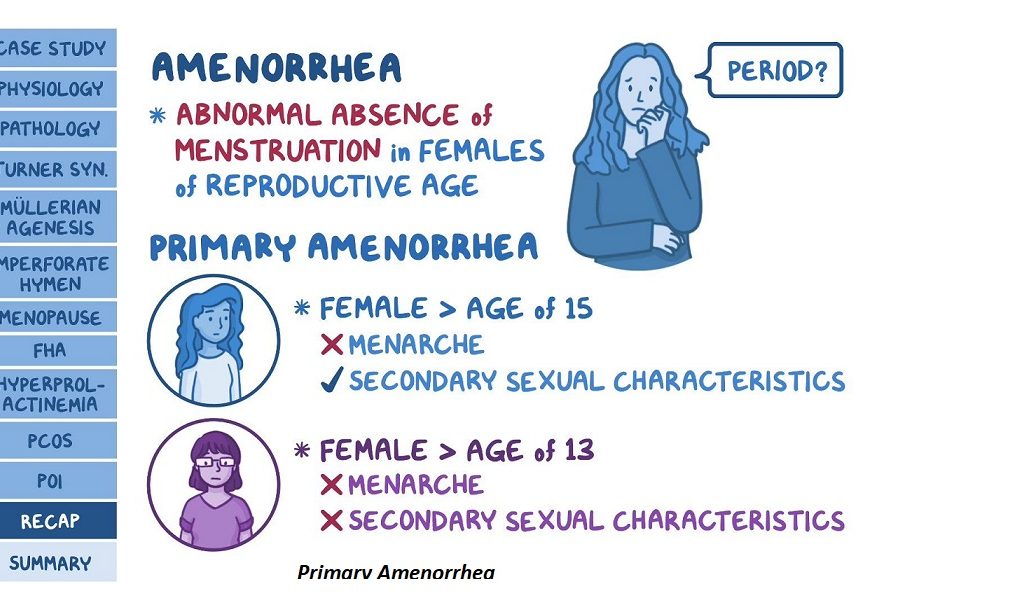
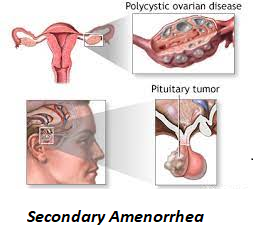
Secondary Amenorrhea: Secondary amenorrhea refers to the cessation of menstruation in women who previously had regular periods. Potential causes encompass pregnancy, stress, extreme weight loss or gain, thyroid disorders, and polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS).
Causes:
Natural : Pregnancy, Breastfeeding and Menopause.
Hormonal Imbalances: Hormonal disruptions, such as those caused by thyroid disorders, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), and pituitary gland problems, can result in no period.
Stress and Emotional Factors: High levels of stress, anxiety, or emotional trauma can impact the hypothalamus, disrupting the cycle.
Extreme Weight Changes: Rapid weight loss or excessive weight gain can affect hormonal balance and lead to cessation of period.
Contraceptives: Some may experience amenorrhea due to birth control pills; normal ovulation and menstruation may take time to resume after discontinuation.
Medications: Antidepressant, Antipsychotic medications , blood pressure medicines, Cancer chemotherapy, Allergy medications .
Excessive Exercise: Rigorous training in activities like ballet may contribute to amenorrhea due to factors such as low body fat, stress, and high energy expenditure.
 |
| Causes |
Risk Factor :
Risk factors for cessation of period include:
- Family history or early menopause.
- Genetic or chromosomal condition that affects your ovaries or uterus.
- Obesity or being underweight.
- Eating disorder.
- Over-exercising.
- Poor diet.
- Stress.
- Chronic illness.
Symptoms of amenorrhea :
The main symptom is the absence of menstruation. Other symptoms may vary depending on the underlying cause. Some common symptoms include:
- Hot flashes
- Night sweats
- Vaginal dryness
- Acne
- Excess hair growth
- Breast tenderness
- Headaches
- Mood swings
- Difficulty sleeping.
 |
| Symptoms |
Complications :
It has various complications, especially if left untreated or if it results from an underlying medical condition. Here are some potential complications :
Infertility: Amenorrhea, particularly when caused by conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) or hypothalamic amenorrhea, can significantly reduce the chances of conception and pregnancy.
Osteoporosis: Prolonged amenorrhea, especially if it occurs during the peak bone-building years of adolescence and early adulthood, can lead to decreased bone density and increase the risk of osteoporosis, making bones more susceptible to fractures.
Cardiovascular Issues: Hormonal imbalances, especially in cases like PCOS or premature ovarian failure, can increase the risk of cardiovascular problems, such as high blood pressure and abnormal lipid profiles.
Uterine Issues: lack of menses due to anovulation (lack of ovulation), there may be an increased risk of uterine conditions, including endometrial hyperplasia, which can potentially lead to endometrial cancer.
Psychological and Emotional Impact: The emotional and psychological impact of no period can be significant. Women may experience distress, anxiety, and depression due to fertility concerns, body image issues, or the underlying causes of amenorrhea, such as eating disorders.
Hormonal Imbalances: It often linked to hormonal imbalances, which can affect various aspects of health, including mood, energy levels, and overall well-being.
Metabolic Changes: Some conditions leading to period cessation, like PCOS and hypothalamic amenorrhea, can be associated with insulin resistance and metabolic syndrome, which increase the risk of type 2 diabetes.
Adverse Effects on Reproductive Organs: In some cases, the absence of period may be due to structural issues or tumors in the reproductive organs. These conditions may require surgical intervention and can have associated complications.
Impact on Quality of Life: The absence of menstrual cycles can affect a woman’s sense of femininity and may lead to social and emotional challenges, impacting overall quality of life.
Hormone Replacement Therapy Risks: In cases where hormone replacement therapy is used , there may be associated risks, such as an increased risk of blood clots, depending on the type of hormones used and individual factors.

Diagnosis :
Healthcare provider will perform a pelvic exam to check for any problems related to reproductive organs. If never had a period, healthcare provider may examine your breasts and genitals to see if you’re experiencing the normal changes of puberty.
Tests ;
- Pregnancy test .
- Blood test : To check hormones level along with thyroid and adrenal gland disorder.
- Genetic testing : to look for primary ovarian insufficiency and 40 or younger age group .
- MRI : If suspecting a defect in pituitary gland.
- Ultrasound : To rule out any pathology in ovaries or uterus .
Management:
The treatment will vary depending on the underlying cause. Once your healthcare provider has identified the cause, they can recommend the best course of treatment for you.
If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, amenorrhea is normal and no treatment is necessary. If you are taking birth control pills or other hormonal contraceptives, your healthcare provider may recommend changing your method of birth control or stopping contraception altogether.
For other causes , treatment may include:
- Weight loss or gain
- Changes in exercise habits
- Stress management
- Hormone therapy
- Medication
- Surgery
Conclusion :
Amenorrhea can be a distressing condition, but it is important to remember that it is usually treatable. If you are experiencing see your doctor to determine the underlying cause and get the appropriate treatment.
In addition to the above, here are some other important things to keep in mind:
It can increase your risk of osteoporosis, a condition that causes weak and brittle bones. It is important to talk to your doctor about ways to reduce your risk of osteoporosis, such as taking calcium and vitamin D supplements and exercising regularly.
If you are trying to get pregnant and you have no period, it is important to see a doctor to determine the underlying cause and get the appropriate treatment.
If you have no period, it is important to talk to your doctor about your concerns and to get support from your loved ones. Cessation of period can be a challenging condition, but it is important to remember that you are not alone.

Frequently Asked Questions ( FAQs) ;
Amenorrhea is the absence of menstrual periods in women of reproductive age, defined as missing one or more menstrual cycles.
Causes include pregnancy, hormonal imbalances (e.g., thyroid disorders, PCOS), stress, extreme weight changes, contraceptives, medications, and excessive exercise.
Primary amenorrhea occurs when a girl doesn't start menstruating by age 16, and secondary amenorrhea refers to the cessation of periods in women who previously had regular cycles.
Consult a healthcare provider if you experience the absence of menses, especially if accompanied by other symptoms or risk factors.
Diagnosis involves a thorough evaluation, including medical history, physical examination, pregnancy tests, hormonal assessments, imaging studies, and sometimes a biopsy.
Risk factors include family history of early menopause, genetic conditions, obesity, being underweight, eating disorders, over-exercising, poor diet, stress, and chronic illness.
Yes, high levels of stress, anxiety, or emotional trauma can impact the hypothalamus, disrupting the menstrual cycle and leading to amenorrhea.
Treatment depends on the underlying cause and may involve addressing hormonal imbalances, nutritional deficiencies, lifestyle modifications, medications, or hormone therapy.
Complications may include infertility, an increased risk of osteoporosis, and mental health issues such as stress and depression.
Amenorrhea is normal during pregnancy and menopause. However, any deviation from a normal menstrual pattern should be discussed with a healthcare professional.
Yes, certain medications, including antidepressants, antipsychotics, blood pressure medicines, cancer chemotherapy, and allergy medications, may contribute to no menses.
Lifestyle factors such as extreme weight changes, poor diet, and excessive exercise can affect hormonal balance and contribute to the cessation of menstrual periods.
In many cases, it is reversible with appropriate treatment addressing the underlying cause. However, individual outcomes vary.
Some individuals may experience it while taking birth control pills. It may take some time for regular ovulation and menstruation to resume after discontinuation.
Yes, amenorrhea can be associated with symptoms such as hot flashes, night sweats, mood swings, and other hormonal-related changes. What is amenorrhea?
What are the common causes of amenorrhea?
What are the types of amenorrhea?
When should I be concerned about amenorrhea?
How it is diagnosed ?
What are the risk factors ?
Can stress cause amenorrhea?
How it is treated?
Are there complications associated with amenorrhea?
Is it common during pregnancy and menopause?
Can medications cause amenorrhea?
How can lifestyle factors impact amenorrhea?
Is amenorrhea reversible?
Can birth control pills cause amenorrhea?
Is it associated with symptoms like hot flashes and mood swings?
These FAQs provide general information, and individuals experiencing amenorrhea or related concerns should consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice and guidance.