Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental condition affecting millions of children and adults worldwide. While often associated with childhood, ADHD frequently persists into adulthood, impacting work, relationships, and daily life. This guide covers early signs, diagnosis, treatment options, and practical management strategies at every age.
Types of ADHD
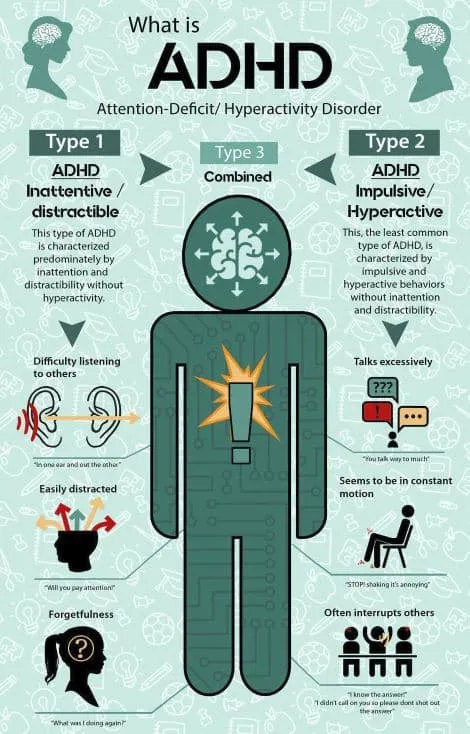
Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity. The DSM-5 (Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th Edition) recognizes three primary presentations (previously called “subtypes”) of ADHD:
1. Predominantly Inattentive Presentation (ADHD-PI)
- Key Symptoms:
- Difficulty sustaining attention
- Easily distracted
- Forgetfulness in daily activities
- Trouble organizing tasks
- Avoidance of tasks requiring prolonged focus
- Often seems not to listen when spoken to directly
- Common Traits:
- May appear daydreamy or “spacey”
- Often misdiagnosed as a learning disability or anxiety
- More common in girls and adults
2. Predominantly Hyperactive-Impulsive Presentation (ADHD-HI)
- Key Symptoms:
- Excessive fidgeting or restlessness
- Difficulty staying seated (in children, may run or climb excessively)
- Talking excessively
- Interrupting others (blurting out answers)
- Difficulty waiting their turn
- Acts as if “driven by a motor”
- Common Traits:
- More noticeable in young children
- May decrease with age, transitioning to impulsivity
3. Combined Presentation (ADHD-C)
- Key Symptoms:
- Meets criteria for both inattentive and hyperactive-impulsive symptoms
- Common Traits:
- Most commonly diagnosed type
- Significant challenges in focus, impulse control, and activity regulation
Additional Notes:
- ADHD in Adults: Often presents as inattentiveness, disorganization, and impulsivity rather than hyperactivity.
- Sluggish Cognitive Tempo (SCT): A proposed subtype (not yet in DSM) with symptoms like slow processing, daydreaming, and lethargy.
- Emotional Dysregulation: Some researchers suggest this as a core feature, though not officially a subtype.
Early Signs in Children and Adults
Recognizing the early signs is crucial for timely intervention. Symptoms often appear in childhood, but many go undiagnosed until adulthood. Below, we break down the key red flags by age group.
🚩 Early Signs of ADHD in Children (Ages 3-12)
🔹 Inattentive Symptoms
- Short attention span – Struggles to focus on tasks (e.g., homework, play).
- Easily distracted – Loses track of conversations or instructions.
- Forgetfulness – Frequently loses belongings (backpacks, jackets).
- Avoids mentally demanding tasks – Resists reading or puzzles.
🔹 Hyperactive/Impulsive Symptoms
- Excessive fidgeting – Can’t sit still, taps hands or feet.
- Running/climbing excessively – Even in inappropriate settings.
- Blurting out answers – Interrupts conversations or games.
- Difficulty waiting turns – Struggles in group activities.
📌 Real-Life Example:
A 7-year-old may:*
- Forget to turn in homework despite completing it.
- Constantly interrupt story time at school.
- Leave their seat during class without permission.
🚩 Early Signs of ADHD in Teens & Adults
Many assume Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder is a “childhood disorder,” but ~60% of cases persist into adulthood, often with subtler symptoms:
🔹 Inattentive Symptoms
- Chronic disorganization – Missed deadlines, cluttered workspaces.
- Procrastination – Delays tasks until the last minute.
- Frequent careless mistakes – At work or in daily responsibilities.
- Zoning out mid-conversation – Mind wanders during meetings.
🔹 Hyperactive/Impulsive Symptoms (Less Obvious in Adults)
- Restlessness – Taps pens, shakes legs, or feels “on edge.”
- Impulsive decisions – Overspending, quitting jobs abruptly.
- Interrupting others – Struggles to wait their turn in discussions.
📌 Real-Life Example:
An adult with undiagnosed ADHD may:*
- Start multiple projects but rarely finish them.
- Forget important dates (anniversaries, bills).
- Struggle to follow through on commitments.
🔍 Why Early Detection Matters
- Kids: Early support improves academic performance and social skills.
- Adults: Diagnosis reduces risks of job instability, anxiety, and depression.
⚠️ When to Seek Help:
If symptoms:
- Persist for 6+ months.
- Occur in multiple settings (home, school, work).
- Interfere with daily life or relationships.
🧩 ADHD vs. Similar Conditions
Some symptoms overlap with:
- Anxiety (trouble focusing due to worry).
- Learning disabilities (e.g., dyslexia).
- Sleep disorders (fatigue mimics inattention).
A professional assessment is key for accurate diagnosis.
🗝️ Key Takeaways
✔ ADHD signs appear before age 12—but may go unnoticed.
✔ Hyperactivity decreases with age, but inattention often remains.
✔ Early intervention leads to better long-term outcomes.
Think you or your child might have ADHD? Take our quick screener: https://psychcentral.com/quizzes/adhd-quiz
🔍 ADHD Diagnosis Process
1. Initial Screening
- Who does it? Pediatricians, primary care doctors, or mental health specialists.
- What happens?
- Review of symptoms (using DSM-5 criteria).
- Discussion of medical/family history (ADHD is 74-90% genetic).
2. Behavioral Assessments
- For Children:
- Parent/teacher questionnaires (e.g., Vanderbilt Assessment Scale).
- School performance review (missing assignments, disruptive behavior).
- For Adults:
- Self-report scales (e.g., Adult ADHD Self-Report Scale – ASRS).
- Interviews about childhood behavior (since ADHD starts before age 12).
Free ADHD Symptom Checklist for Adults: https://www.caddra.ca/wp-content/uploads/ASRS.pdf
📋 Diagnostic Criteria (DSM-5)
A patient must show:
✔ 6+ symptoms of inattention or hyperactivity-impulsivity (for children).
✔ 5+ symptoms (for adults).
✔ Symptoms lasting ≥6 months.
✔ Impairment in two+ settings (home, school, work).
Subtypes
- Predominantly Inattentive (struggles with focus, organization).
- Predominantly Hyperactive-Impulsive (fidgety, impulsive actions).
- Combined Type (both inattentive and hyperactive symptoms).
🧪 Medical Tests (To Rule Out Other Conditions)
- Blood tests – Check for thyroid issues or vitamin deficiencies.
- Hearing/vision tests – Ensure sensory problems aren’t causing symptoms.
- Sleep studies – Rule out sleep apnea (can mimic ADHD inattention).
Note: There’s no single ADHD test (like a blood test or brain scan). Diagnosis relies on behavioral observations and history.
👩⚕️ Who Can Diagnose?
- Children: Pediatricians, child psychologists, psychiatrists.
- Adults: Psychiatrists, neurologists, ADHD specialists.
🚩 Red Flags in Diagnosis:
- A doctor who diagnoses ADHD in one 10-minute visit.
- Clinics that only prescribe meds without therapy options.
🗝️ Key Takeaways
✔ ADHD diagnosis requires a detailed history (not just a quick test).
✔ Multiple sources (parents, teachers, self-reports) improve accuracy.
✔ Rule out other conditions first (sleep disorders, anxiety, learning disabilities).
Think you might have ADHD? Start with ADHD Self-Test : https://www.clinical-partners.co.uk/for-adults/adult-adhd-add/test-for-adhd
💊 Medication
1. Stimulants (First-Line Treatment)
- How they work: Increase dopamine/norepinephrine to improve focus.
- Common types include Methylphenidate and Amphetamines .
- Effectiveness: Help 70-80% of people with ADHD but there is a risk of abuse.
2. Non-Stimulants (For Those Who Can’t Tolerate Stimulants)
- Examples:
- Atomoxetine – Good for anxiety comorbidity.
- Guanfacine – Helps with impulsivity.
- Pros: No risk of abuse; lasts 24 hours.
3. Antidepressants (For ADHD + Depression/Anxiety)
- Example: Bupropion (Wellbutrin) – Boosts dopamine/norepinephrine.
Disclaimer
The following information is intended for educational purposes only and does not replace professional medical advice. Self-medication for Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder—or any health condition—can be dangerous, ineffective, or life-threatening.
🧠 Behavioral & Psychological Therapies
For Children:
- Parent Training – Teaches behavior-modification techniques.
- School Interventions – IEP/504 plans for extra time, breaks, or seating adjustments.
- Social Skills Training – Helps kids manage peer interactions.
For Adults:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) – Improves time management, organization, and emotional regulation.
- ADHD Coaching – Provides accountability for daily tasks.
🏆 Lifestyle & Natural Management Strategies
1. Diet & Nutrition
- Protein-rich breakfasts (eggs, Greek yogurt) – Stabilizes focus.
- Omega-3s (salmon, walnuts) – May improve attention.
- Limit sugar/processed foods – Reduces hyperactivity crashes.
2. Exercise & Movement
- Aerobic exercise (30 mins/day) – Boosts dopamine.
- Yoga/meditation – Calms hyperactivity and anxiety.
3. Sleep Hygiene
- Consistent bedtime – ADHD brains need structure.
- No screens before bed – Blue light disrupts sleep.
ADHD-Friendly Meal Plans: https://jackiesilvernutrition.com/articles/adhd-meal-planning-for-adults/
📌 Workplace & School Accommodations
For Students:
- Extended test time.
- Use of fidget tools (stress balls, wobble chairs).
- Breaks during long tasks.
For Adults:
- Noise-canceling headphones for focus.
- Task prioritization apps (Todoist, Trello).
- Flexible work schedules.
🚫 Common Treatment Mistakes
- Relying only on meds – Therapy and lifestyle matter too!
- Inconsistent routines – Structure is key for ADHD brains.
- Ignoring comorbidities – Anxiety/depression often accompany ADHD.
Disclaimer
The information provided in this article is for educational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always consult a qualified healthcare professional (e.g., psychiatrist, neurologist, or pediatrician) before making decisions about Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder management.
FAQs
Is Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder a real disorder?
Yes. it is a neurodevelopmental condition recognized by the: - American Psychiatric Association (DSM-5) - World Health Organization (ICD-11) - CDC, NIH, and global medical institutions.
Can ADHD develop in adulthood?
No, but it may go undiagnosed until adulthood. Symptoms must appear before age 12 for diagnosis.
Is ADHD caused by bad parenting or too much sugar?
Myth. - Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder is genetic (74-90% heritable). - Diet/parenting may worsen symptoms but don’t cause it.
How is Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder diagnosed in adults if it starts in childhood?
Doctors review school records, parent interviews, and self-reports of childhood behavior. Tools like the Wender Utah Rating Scale help assess past symptoms.
Can anxiety/depression mimic ADHD?
Yes. Key differences: - ADHD: Lifelong focus/organization struggles. - Anxiety: Overthinking disrupts focus situationally.
Do Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder meds lead to addiction?
- Stimulants (e.g., Adderall) have abuse potential but <1% of ADHD patients develop addiction when taken as prescribed. - Non-stimulants (e.g., Strattera) are non-addictive.
Can ADHD be managed without medication?
Yes. Behavioral therapy, exercise, and organizational strategies help, but meds are most effective for severe cases.
What foods help ADHD?
- Best: Protein, omega-3s (salmon, walnuts), iron-rich foods (spinach). - Avoid: Sugar crashes worsen focus.
Is ADHD overdiagnosed?