The Keto Diet: A Comprehensive Guide to Types, Mechanism, Benefits, Risks, and a Daily Meal Plan
The ketogenic diet, or keto diet, has surged in popularity over the last few years as a powerful tool for weight loss and overall health improvement. But what exactly is the keto diet, how does it work, and what are its potential benefits and risks? This detailed guide will explore the various aspects of the keto diet, including its types, the science behind it, potential health benefits and risks, and a sample meal plan to help you get started.
What is the Keto Diet?
The ketogenic diet is a high-fat, low-carbohydrate diet designed to shift the body into a state of ketosis, where fat becomes the primary source of energy instead of carbohydrates. By significantly reducing carbohydrate intake and increasing fat consumption, the body is forced to use fat stores for energy, leading to potential weight loss and other health benefits.
How it Works?
The ketogenic diet, commonly known as the keto diet, works by fundamentally changing the way your body uses energy. Here’s a detailed explanation of how it works:
1. Shift from Carbohydrates to Fats as the Primary Energy Source
Under normal dietary conditions, your body primarily relies on carbohydrates (in the form of glucose) for energy. When you eat foods rich in carbohydrates, they are broken down into glucose, which is then used by your cells for energy. Any excess glucose is stored in the liver and muscles as glycogen.
However, when you follow a keto diet, your carbohydrate intake is drastically reduced, typically to about 20-50 grams per day. This is much lower than what most people consume on a regular diet, which can range from 200-300 grams of carbs per day. With such low carbohydrate intake, your body’s glycogen stores become depleted.
2. Entering Ketosis
When glycogen stores are depleted, your body needs to find an alternative source of energy. This is where ketosis comes into play. Ketosis is a metabolic state in which the liver starts converting stored fats into molecules called ketones. These ketones then become the primary source of energy for the body, replacing glucose.
- Ketone Production: The liver breaks down fatty acids into ketones. The three main types of ketones are:
- Acetoacetate
- Beta-hydroxybutyrate (BHB)
- Acetone
Acetoacetate and BHB are used as energy sources, while acetone is a byproduct that is excreted from the body, often detected in the breath.
3. Fat as Fuel
Once your body is in ketosis, it becomes highly efficient at burning fat for energy. This fat can come from both dietary sources (the fats you eat) and stored body fat. This shift is one of the main reasons why the keto diet is often associated with weight loss, as the body starts to burn its fat reserves for fuel.
4. Steady Energy Supply
One of the benefits of using ketones for energy is that it provides a more consistent and steady energy supply compared to glucose. When your body relies on glucose, energy levels can fluctuate, leading to highs and lows (commonly known as sugar crashes). In ketosis, the energy from ketones is more stable, which can lead to improved mental clarity, focus, and sustained physical energy.
5. Reduction in Insulin Levels
Insulin is a hormone that helps regulate blood sugar levels. On a high-carbohydrate diet, insulin levels can spike after meals as the body tries to manage the influx of glucose. However, on a keto diet, with very few carbohydrates being consumed, insulin levels remain low and stable. This can be particularly beneficial for individuals with insulin resistance or type 2 diabetes, as it helps improve blood sugar control.
6. Appetite Suppression
The keto diet can also lead to a natural reduction in appetite. Fats and proteins are more satiating than carbohydrates, which means you may feel fuller for longer periods. This reduction in hunger can contribute to lower overall calorie intake, further aiding in weight loss.
7. Enhanced Fat-Burning During Exercise
For those who exercise, especially in endurance sports, the keto diet can enhance fat oxidation during physical activity. As your body becomes more adapted to burning fat for fuel, it becomes more efficient at doing so even during intense exercise, which can improve performance in endurance-based activities.
8. Adaptation Phase
It’s important to note that when you first start the keto diet, your body may take some time to adapt to this new way of obtaining energy. This adaptation phase, often referred to as the “keto flu,” can involve symptoms such as headache, fatigue, irritability, and nausea as your body adjusts to burning fat instead of carbs. These symptoms usually subside within a few days to a week as your body becomes fully adapted to ketosis.
Types of Keto Diets:
- Standard Ketogenic Diet (SKD): The most common form, consisting of very low carbs, moderate protein, and high fat.
- Cyclical Ketogenic Diet (CKD): Involves periods of higher-carb refeeds, such as 5 ketogenic days followed by 2 high-carb days.
- Targeted Ketogenic Diet (TKD): Allows for eating more carbs around workouts to fuel exercise performance.
- High-Protein Ketogenic Diet: Similar to SKD but includes more protein, with a ratio of about 60% fat, 35% protein, and 5% carbs.
Health Benefits:
The ketogenic diet offers a variety of health benefits, particularly for those looking to lose weight, manage blood sugar levels, and improve overall health. Here are some of the key benefits of the keto diet:
1. Weight Loss
- Fat Burning: The keto diet plan helps the body become efficient at burning fat for energy. As the body shifts into ketosis, it starts using stored fat as the primary fuel source, which can lead to significant weight loss, especially in the early stages.
- Appetite Suppression: High-fat and high-protein foods are more satiating than carbohydrates, helping to reduce overall calorie intake. Many people on the keto diet food experience reduced hunger, making it easier to maintain a calorie deficit.
- Reduced Insulin Levels: Lower insulin levels promote fat burning. When carbohydrate intake is low, insulin production drops, allowing the body to release stored fat more effectively.
- When it comes to weight loss, which is often a primary reason many people try the ketogenic diet, the benefits may not be significantly different from other diet plans.
According to Spano, “There isn’t a unique weight loss advantage that comes solely from the ketogenic diet.” - The diet may promote weight loss similarly to other diets by limiting food choices, thereby reducing overall calorie intake.
- Chris Mohr, a sports dietitian based in Louisville, Kentucky, and co-owner of MohrResults.com, echoes this sentiment. He explains that “reducing carbohydrates drastically results in a significant calorie reduction,” which initially leads to a loss of water weight. This rapid change often appeals to individuals seeking quick results. However, Mohr notes that the overall calorie reduction isn’t always guaranteed, as the diet’s emphasis on fat can lead to higher consumption of calorie-dense foods.
2. Improved Blood Sugar Control
- Stabilized Blood Sugar Levels: By minimizing carbohydrate intake, the keto diet helps prevent spikes and crashes in blood sugar levels. This can be particularly beneficial for people with type 2 diabetes or insulin resistance.
- Improved Insulin Sensitivity: The keto diet can improve the body’s sensitivity to insulin, making it more efficient at managing blood sugar levels. This can help reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes and may help manage the condition in those who already have it.
3. Enhanced Mental Clarity and Focus
- Steady Energy Supply: The consistent energy provided by ketones (rather than glucose) helps avoid the mental fog and energy crashes often associated with high-carb diets. Many people on the keto diet report improved cognitive function, focus, and mental clarity.
- Neuroprotective Effects: Ketones are a more efficient fuel source for the brain than glucose, and some studies suggest that the keto diet may have neuroprotective benefits, potentially helping to prevent or manage conditions like Alzheimer’s disease.
4. Increased Energy Levels
- More Efficient Fat Burning: Once the body adapts to ketosis, it becomes highly efficient at burning fat for fuel, which can lead to more sustained energy throughout the day.
- Better Endurance Performance: For athletes and active individuals, the keto diet can enhance endurance by increasing the availability of fat as a fuel source during prolonged physical activity.
5. Reduced Inflammation
- Anti-Inflammatory Effects: The keto diet may help reduce inflammation in the body, which is linked to a variety of chronic diseases, including heart disease, cancer, and autoimmune conditions. The reduction in carbohydrate intake, especially refined sugars and processed foods, is thought to be a contributing factor..
6. Better Management of Certain Health Conditions
- Epilepsy: The keto diet was originally developed as a treatment for epilepsy, particularly in children who do not respond well to other treatments. It has been shown to significantly reduce the frequency of seizures in some individuals.
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): Some evidence suggests that the keto diet may help improve symptoms of PCOS, such as insulin resistance and hormonal imbalances.
- Certain Neurological Disorders: Research is ongoing, but there is some evidence that the keto diet may benefit individuals with conditions such as Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease, and traumatic brain injuries.
7. Potential for Cancer Treatment
- Starving Cancer Cells: Some research suggests that the keto diet may help starve cancer cells by depriving them of glucose, their primary fuel source. While more research is needed, the keto diet is being studied as a potential complementary therapy for cancer treatment.
8. Appetite Control and Satiety
- Reduced Cravings: The keto diet can help reduce cravings for sugary and high-carb foods, making it easier to stick to the diet and avoid overeating.
- Longer Satiety: High-fat and high-protein foods take longer to digest, keeping you feeling fuller for longer periods, which can aid in weight management.
9. Potential Improvement in Skin Health
- Reduced Acne: Some people on the keto diet report improvements in skin health, particularly a reduction in acne. This may be due to lower insulin levels and reduced sugar intake, both of which can influence skin health.
Risk and Considerations
While the ketogenic diet has several potential benefits, it also comes with risks and considerations that should be taken into account before starting. Here’s a detailed look at the potential downsides and challenges of the keto diet:
1. Keto Flu
- What It Is: The “keto flu” refers to a group of symptoms that some people experience when they first start the keto diet. These symptoms can include headache, fatigue, nausea, dizziness, irritability, difficulty sleeping, and constipation.
- Why It Happens: Keto flu occurs as the body adjusts to burning fat for fuel instead of carbohydrates. The sudden drop in carbohydrate intake can cause imbalances in electrolytes and water, leading to these symptoms.
- How to Mitigate: Staying hydrated, increasing salt intake, and ensuring adequate intake of electrolytes (sodium, potassium, magnesium) can help alleviate keto flu symptoms. Gradually reducing carb intake rather than cutting it drastically may also ease the transition.
2. Nutrient Deficiencies
- Potential Deficiencies: The keto diet restricts certain food groups, particularly fruits, vegetables, and grains, which are rich in essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber. This can lead to deficiencies in important nutrients such as:
- Fiber: Essential for digestive health.
- Vitamins: Such as vitamin C, vitamin D, and B vitamins.
- Minerals: Including magnesium, potassium, and calcium.
- How to Mitigate: It’s important to incorporate low-carb, nutrient-dense foods such as leafy greens, nuts, seeds, and avocados. Some people may also need to take supplements to ensure they meet their nutritional needs.
3. Digestive Issues
- Common Problems: The high-fat content of the keto diet can lead to digestive issues, such as constipation, diarrhea, or bloating, especially if your body is not used to processing large amounts of fat.
- Why It Happens: A lack of fiber-rich foods and an abrupt increase in fat intake can disrupt digestion.
- How to Mitigate: Gradually increase fat intake to allow your digestive system to adapt, and include plenty of low-carb, fiber-rich vegetables to support gut health. Drinking plenty of water and considering fiber supplements may also help.
4. Increased Cholesterol Levels
- Potential Risks: While many people experience improvements in cholesterol levels on the keto diet, some may see an increase in LDL (bad) cholesterol, which could raise the risk of heart disease in certain individuals.
- How to Mitigate: Focus on consuming healthy fats (like those from olive oil, avocados, and nuts) rather than saturated fats from sources like red meat and butter. Regularly monitor cholesterol levels, and consult with a healthcare provider if you have pre-existing heart conditions.
5. Risk of Ketoacidosis
- What It Is: Ketoacidosis is a dangerous metabolic condition where the body produces excessively high levels of ketones, leading to an overly acidic blood pH. It is more common in people with type 1 diabetes.
- Why It Happens: This condition is rare on a well-formulated keto diet, but it can occur if insulin levels are too low, causing an uncontrolled increase in ketone production.
- How to Mitigate: People with diabetes or those on medication should consult with their healthcare provider before starting the keto diet to monitor ketone levels and prevent complications.
6. Long-Term Sustainability
- Challenges: The restrictive nature of the keto diet can make it difficult to maintain in the long term. Many people find it challenging to adhere to the diet’s strict guidelines, leading to potential yo-yo dieting, where individuals repeatedly lose and regain weight.
- How to Mitigate: Consider whether the keto diet aligns with your lifestyle and preferences. Some may find success with a modified or cyclical approach to keto, or by transitioning to a less restrictive low-carb diet after achieving initial goals.
7. Impact on Physical Performance
- Short-Term: During the initial adaptation phase, some people experience a decrease in physical performance, particularly in high-intensity activities, as the body adjusts to burning fat instead of glucose for energy.
- Long-Term: While endurance performance may improve, activities that rely heavily on quick bursts of energy (like sprinting or heavy lifting) might be negatively affected.
- How to Mitigate: Athletes or those who engage in intense workouts might benefit from the Targeted Ketogenic Diet (TKD) or the Cyclical Ketogenic Diet (CKD), which allow for strategic carb intake around workouts.
8. Potential Impact on Bone Health
- Risk: Some studies suggest that the keto diet may lead to decreased bone density over time, possibly due to changes in mineral balance and reduced intake of bone-supporting nutrients.
- How to Mitigate: Ensure adequate intake of calcium, vitamin D, and magnesium, and consider resistance training to support bone health.
9. Social and Lifestyle Implications
- Challenges: The strict dietary restrictions can make social eating situations, dining out, and family meals challenging, which may lead to feelings of isolation or frustration.
- How to Mitigate: Plan ahead by finding keto-friendly options at restaurants, or bringing your own dishes to social gatherings. Communication with family and friends about your dietary choices can also help in navigating social situations.
10. Potential Hormonal Changes
- Concerns for Women: Some women may experience changes in menstrual cycles, fertility, or other hormone-related issues on the keto diet, particularly if calorie intake is too low or if the diet is followed too strictly.
- How to Mitigate: Women should pay attention to their body’s signals and consider adjusting fat, protein, and carb intake if they experience hormonal imbalances. Consulting with a healthcare provider or nutritionist can provide personalized guidance.
Keto Diet Meal Plan
Here’s a simple one-day keto meal plan that you can follow. This plan is designed to keep you in ketosis while providing a balance of healthy fats, moderate protein, and low carbohydrates.
Keto Diet Breakfast
Scrambled Eggs with Spinach and Avocado
- 3 large eggs, scrambled in butter or olive oil
- 1/2 cup fresh spinach, sautéed with the eggs
- 1/2 avocado, sliced
- Salt and pepper to taste
Optional: Coffee or tea with 1 tablespoon of heavy cream or coconut oil
Keto diet Lunch
Grilled Chicken Salad
- 4-6 oz grilled chicken breast, sliced
- 2 cups mixed greens (lettuce, spinach, arugula)
- 1/4 cup cherry tomatoes, halved
- 1/4 cup cucumber slices
- 1/4 avocado, sliced
- 1-2 tablespoons olive oil and vinegar dressing
Keto Diet best Snack
Cheese and Nuts
- 1 oz of cheese (cheddar, mozzarella, or your choice)
- A small handful of nuts (almonds, walnuts, or macadamia nuts)
Keto Diet Dinner
Baked Salmon with Asparagus
- 4-6 oz salmon fillet, seasoned with salt, pepper, and lemon
- 1 tablespoon of olive oil or butter for cooking
- 1 cup asparagus, roasted with olive oil, garlic, and parmesan cheese
Side Salad:
- 1 cup mixed greens
- 1 tablespoon olive oil, and 1 teaspoon balsamic vinegar dressing
Dessert (Optional)
Keto Chocolate Fat Bomb
- 1 tablespoon coconut oil
- 1 tablespoon unsweetened cocoa powder
- 1 teaspoon stevia or another keto-friendly sweetener
- Mix and freeze for a quick, satisfying treat
Beverages
- Water, herbal tea, or sparkling water throughout the day
- Coffee or tea with heavy cream (optional)
This meal plan provides a balance of fats, proteins, and low carbs, helping you stay in ketosis while enjoying flavorful, satisfying meals. Adjust portions as needed based on your personal calorie and nutritional requirements.
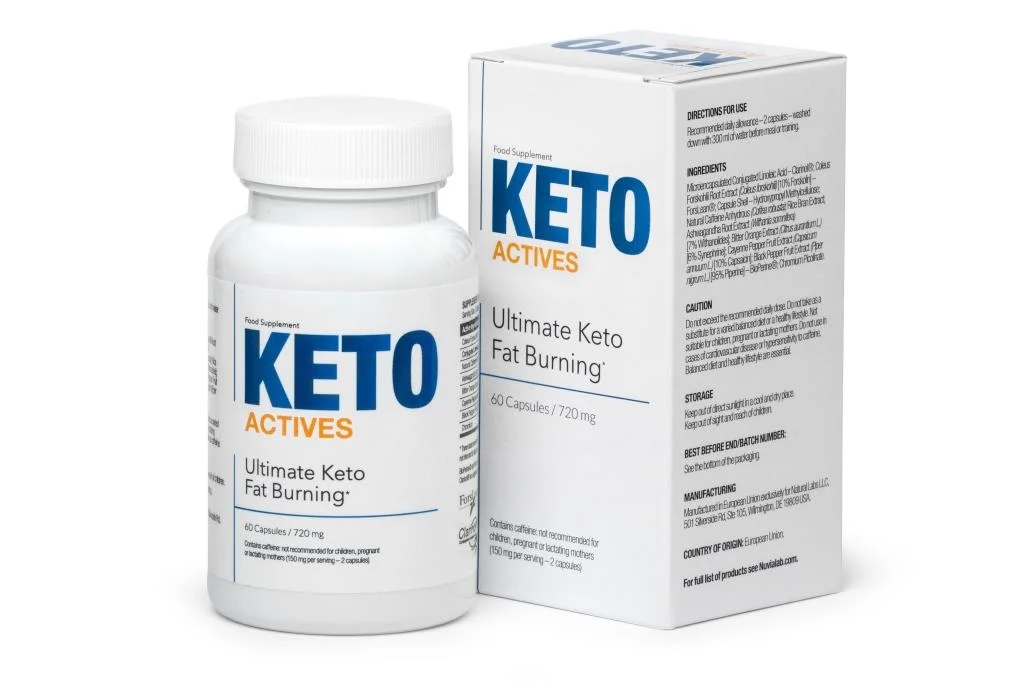
Keto Actives
Keto Actives is a dietary supplement marketed to support weight loss, particularly for people following a ketogenic diet. It aims to enhance fat burning, reduce appetite, and increase energy levels by utilizing natural ingredients that support ketosis. Here’s a breakdown of what Keto Actives typically includes and how it works:
Key Ingredients
- ForsLean® (Coleus Forskohlii Root Extract): Known for stimulating fat metabolism and promoting lean body mass.
- Clarinol® (Conjugated Linoleic Acid – CLA): A fatty acid that helps reduce body fat by enhancing fat oxidation and metabolism.
- Caffeine Anhydrous: Acts as a stimulant to boost energy, increase thermogenesis, and improve exercise performance.
- Bitter Orange Extract: Contains synephrine, which may help suppress appetite and increase metabolic rate.
- Black Pepper Extract (Piperine): Enhances the absorption of other nutrients, improving their effectiveness.
- Ashwagandha Root Extract: Helps to balance stress hormones, which may help in managing weight.
- Chromium: Aids in controlling blood sugar levels, reducing cravings for sweets and carbohydrates.
How Keto Actives Works
Keto Actives is designed to complement the effects of the ketogenic diet, where the body uses fat as the primary energy source instead of carbohydrates. The ingredients aim to:
- Enhance Fat Burning: By boosting the metabolism and promoting fat oxidation, it helps your body burn stored fat more effectively.
- Reduce Appetite: Ingredients like bitter orange extract and chromium help in controlling hunger, making it easier to maintain a calorie deficit.
- Increase Energy: The supplement’s caffeine content increases energy levels, especially important in the early stages of ketosis when some people experience fatigue.
Benefits
- Supports Ketosis: Accelerates fat burning, aiding in quicker weight loss.
- Improves Metabolism: Helps increase metabolic rate, making it easier to burn calories.
- Controls Appetite: Reduces food cravings, helping to stick to the keto diet more easily.
- Boosts Energy: Provides an energy boost, especially useful during exercise.
Considerations
- Side Effects: The caffeine and synephrine content may cause jitters, insomnia, or an increased heart rate in sensitive individuals.
- Not a Replacement for Diet: Keto Actives is intended to supplement a ketogenic diet and exercise routine. It may not be effective without proper diet control.
Who Can Benefit from Keto Actives?
- People on a Ketogenic Diet: It’s specifically designed to support individuals following a keto lifestyle.
- Athletes or Active Individuals: The energy-boosting effects of Keto Actives can enhance performance during workouts.
- Those Looking to Lose Weight: Its fat-burning properties can complement other weight loss efforts.
METHOD OF USE: The recommended daily allowance is 2 capsules, preferably 30 minutes
before a meal. Drink about 300 ml of water with the formula.
WARNINGS: Do not exceed the recommended daily dose. Do not take as a substitute for a
varied balanced diet or a healthy lifestyle. Not suitable for children, pregnant or lactating
mothers. Do not use in cases of cardiovascular disease or hypersensitivity to caffeine.
Balanced diet and healthy lifestyle are essential.
STORAGE: Store in a dry place at room temperature in a tightly closed container. Store out of
reach of small children.
Before using Keto Actives or any supplement, it’s always recommended to consult with a healthcare provider to ensure it aligns with individual health needs and goals.
Keto Diet Shopping List:
Here are some foods that keto diet for beginners should consider adding to their keto diet grocery list:
Proteins
- Poultry
- Red meat
- Seafood
- Nuts and seeds
- Soybeans
Produce
- Spinach
- Asparagus
- Bean sprouts
- Eggplant
- Squash
Eggs and Dairy
- Eggs
- Cheese
- Butter
- Greek yogurt
Condiments
- Salt
- Pepper
- Mayonnaise
- Mustard
- Hot sauce
Drinks
- Tea
- Coffee
- Water
- Nondairy milk
- Coconut water
- keto diet smoothies
Foods to Avoid or Limit:
- Processed snacks such as crackers, corn chips, and potato chips
- Sugary treats like candy, cookies, brownies, and cake
- All types of grains, including bread, pasta, rice, and quinoa
- High-carb fruits, particularly melons and tropical fruits
Keto Diet for Beginners: 5 Tips
- Understand What to Eat and Avoid
To make the most of the ketogenic diet, it’s crucial to know which foods are high in carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. Focus on incorporating nutrient-dense options that fit within the diet’s guidelines. - Seek Professional Guidance
Consult with a registered dietitian to ensure you follow the diet in a healthy manner and minimize the risk of complications or adverse effects. You can find a registered dietitian through resources like EatRight.org. - Be Aware of Potential Side Effects
When starting the keto diet, you may experience symptoms like lethargy, mental fog, constipation, or diarrhea due to changes in fiber intake. These effects usually subside as your body adjusts, but consult your healthcare provider if symptoms persist. - Choose the Right Start Date
Because you may experience initial side effects, select a start date that allows you to ease into the diet without facing pressing deadlines or significant commitments. This will give you time to adjust and manage any symptoms. - Commit to the Long-Term
The ketogenic diet requires a significant and sustained commitment to low carbohydrate intake. Ensure that this diet aligns with your long-term health goals and lifestyle. If maintaining such strict carbohydrate restrictions long-term is unrealistic for you, consider whether this diet is the best choice.
Conclusion
The ketogenic diet offers a unique approach to health management by significantly reducing carbohydrate intake and increasing fat consumption. This shift in macronutrient balance encourages the body to enter a state of ketosis, where it burns fat for fuel instead of glucose. While many people find success with the keto diet, including benefits such as weight loss, improved blood sugar control, and enhanced mental clarity, it is not without its challenges and risks.
Disclaimer: This information provides a general overview of diagnosis, treatment, and medication related to alopecia areata. It is intended to assist in understanding potential options but is not comprehensive. This content is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. It does not cover all possible conditions, treatments, side effects, or risks specific to individual cases. For personalized medical advice, please consult a healthcare provider who can evaluate your unique circumstances. This information does not endorse or validate any specific treatments or medications.
FAQs,
What is Keto diet?
The ketogenic diet is a high-fat, low-carbohydrate diet designed to shift the body into a state of ketosis, where fat becomes the primary source of energy instead of carbohydrates.
Can I get hypoglycaemia in keto diet?
Yes, you can get hypoglycemia on a keto diet, especially in the early stages, as your body adjusts to lower carbohydrate intake and shifts to using fat for energy.
How many carbs on keto diet?
On a keto diet, you typically consume 20-50 grams of net carbs per day.
How much protein on keto diet?
On a keto diet, protein intake typically ranges from 20-25% of your daily calories, which can vary depending on individual needs.