Did you know that about 250 people see dermatologists every day for skin problems1? Your skin’s health is very important. Knowing the early signs of skin cancer can save your life1.
Skin cancer happens when skin cells grow too fast, often because of the sun’s UV rays1. If your family has a history of skin cancer, you’re more likely to get it1. Spotting early symptoms is key to fighting this serious disease.
Melanoma is the most dangerous and deadly skin cancer type1. Checking your skin regularly can help find problems early and save lives1. It’s a good idea to see a dermatologist at least once a year for a full skin check1.
Key Takeaways
- 250 patients are treated daily for skin-related issues
- UV radiation is the primary cause of skin cancer
- Family history increases skin cancer risk
- Early detection is crucial for successful treatment
- Annual dermatologist check-ups are recommended
Understanding Skin Cancer Types and Their Risks
Skin cancer is a serious health concern that affects millions of Americans each year. Knowing the different types of skin cancer helps you spot risks early. This way, you can take steps to detect it early2.
Skin cancer comes in several forms, with basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and melanoma being the most studied. Each type has its own traits and danger levels2.
Basal Cell Carcinoma: The Most Common Skin Cancer
Basal cell carcinoma (BCC) is the most common skin cancer, making up about 80% of all cases2. It often appears in sun-exposed areas, grows slowly, and rarely spreads. It’s most common in people with fair skin2.
Every year, about 3.6 million BCC cases are diagnosed in the United States3. Catching it early is key to treating it successfully.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma: The Second Most Common Type
Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) makes up about 16% of skin cancer cases2. With around 1.8 million cases each year3, SCC is more aggressive than basal cell carcinoma.
Melanoma: The Most Dangerous Form
Melanoma is the most serious skin cancer, making up only 4% of cases but causing most deaths2. Important facts include:
| Statistic | Melanoma Risk |
|---|---|
| Overall Risk | 1 in 38 for white individuals |
| Annual Diagnoses | 99,780 new cases expected in 2023 |
| Five-Year Survival Rate | 99% for localized cases |
Early detection is your best defense against skin cancer progression.
Your risk factors, like sun exposure and genetics, greatly affect your chance of getting skin cancer2.
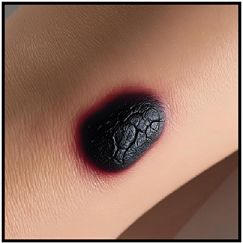
Critical Warning Signs on Your Skin
Finding skin cancer early can save lives. Knowing the warning signs is key to spotting skin lesions early4. About 1 in 5 Americans will get skin cancer, so it’s vital to check your moles often4.
- New or changing moles
- Unusual skin growths
- Non-healing sores
- Itchy or bleeding lesions
- Red or scaly patches
Your body sends out signals if something’s off. Notice any lasting changes in your skin’s look or feel. Some signs to watch for are:
- Moles that change color or size
- Asymmetrical spots
- Irregular border edges
- Lesions larger than 6mm in diameter5
Not every unusual mark is cancer, but it’s always best to get it checked. Melanoma can grow fast, starting from normal skin5. Catching it early can lead to a 99% cure rate5.
| Warning Sign | Potential Significance |
|---|---|
| Color Changes | Possible precursor to skin cancer |
| Asymmetrical Moles | Higher risk of melanoma |
| Non-Healing Sores | Potential skin cancer indicator |
Your skin is huge, and it’s your biggest organ. Regular checks and self-exams can spot problems early. If unsure, see a dermatologist for a professional look.
Changes in Moles and Skin Lesions
It’s important to notice small changes in your skin early. Mole screening helps you keep an eye on your skin’s health6. Most people have moles, but knowing what’s normal can help you stay safe6.
The ABCDE Rule for Melanoma Detection
Dermatologists suggest using the ABCDE rule for mole screening. This method helps spot moles that might be a concern:
- Asymmetry: One half of the mole doesn’t match the other6
- Border: Irregular, ragged, or blurred edges6
- Color: Non-uniform coloration with multiple shades6
- Diameter: Larger than 6 millimeters across6
- Evolving: Changes in size, shape, or color over time6
When Normal Moles Become Suspicious
A normal mole is usually small and stays the same6. If new moles appear or old ones change, see a doctor6. Look out for signs like:
- Spread of pigment beyond the mole’s border
- Redness or swelling
- Changes in sensation
- Surface changes like scaliness or bleeding
Documentation and Tracking Changes
Keeping records can help track changes. Take clear photos of your moles and note any changes. It’s a good idea to get a professional skin screening every year, especially if you’re at higher risk7.
Non-Healing Sores and Persistent Wounds
Your skin’s healing power can tell a lot about your health. Non-healing sores are a big warning sign in dermatology that should not be ignored8. They might show a serious problem, like skin cancer9.
To understand non-healing sores, you need to know what they look like:
- Wounds that stay open for weeks
- Areas with scaly or crusty surfaces
- Lesions that keep bleeding
- Skin areas with unusual texture changes
Some groups are at higher risk for these skin problems. Diabetic patients, for example, are more likely to get chronic ulcers. These can turn into cancer8. It can take about 32 years for this to happen8.
“Any wound that doesn’t heal within a reasonable timeframe demands professional medical evaluation.”
Risk factors for these skin issues include:
- Ultraviolet light exposure
- Previous traumatic injuries
- Chronic inflammatory conditions
- Compromised immune systems
If you see a wound that won’t heal, get a dermatology check-up right away. Early action can greatly improve treatment results and prevent worse problems10.
Unusual Skin Growths and Texture Changes
Your skin can tell you a lot about your health, especially about skin lesions. It’s important to notice small changes in skin texture and color. This can help spot skin cancer risks early11.
Spotting unusual skin growths needs careful watching. Most adults have 10 to 40 moles, but not all are safe11. Look out for these signs:
- Size variations beyond 5 millimeters
- Irregular border shapes
- Multiple color patterns
- Changing or evolving textures
Identifying Suspicious Textures
Skin texture can hint at problems. Watch for these signs:
- Rough, scaly patches
- Raised growths with central depressions
- Firm, red bumps
- Open sores that do not heal
“Early detection is your best defense against skin cancer progression.”
Color Variations and Warning Signs
Color changes are key signs. Look out for dark patches, multi-colored lesions, or sudden color shifts. About 1 in 10 Americans have dysplastic nevi, which raise melanoma risk11.
The risk of melanoma varies by ethnicity. It’s 2.9% for White people, 0.1% for Black people, and 0.5% for Hispanic people11. Knowing these numbers helps you watch your skin more closely.
High-Risk Areas for Skin Cancer Development
Some body parts are more at risk for skin cancer due to sun exposure. Knowing these areas helps you protect your skin better12.
Your face, ears, neck, and hands are at high risk. They get a lot of sun over your lifetime13. People with lighter skin are more likely to get melanoma in these spots12.
- Face and nose
- Ears
- Neck
- Hands and arms
- Shoulders
For those with darker skin, palms, soles, and nail beds are also risky13. These spots are often missed during skin checks.
| Skin Type | High-Risk Areas | Cancer Risk Level |
|---|---|---|
| Fair Skin | Face, Neck, Arms | High |
| Dark Skin | Palms, Soles, Nail Beds | Moderate |
Pro tip: Regular self-checks and using sunscreen on these areas can lower your melanoma risk12.
Sun Exposure and UV Damage Prevention
It’s vital to protect your skin from harmful UV rays to prevent skin cancer. Skin cancer is the most common cancer in the U.S. Knowing about sun exposure and using prevention methods can lower your risk14.
Understanding UV Radiation Risks
UV radiation causes skin cell damage and is a known human carcinogen. About 90% of nonmelanoma skin cancers come from UV exposure1516. The danger is highest between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m. during daylight saving time14.
Protective Measures Against UV Radiation
- Use broad-spectrum sunscreen with SPF 15 or higher14
- Reapply sunscreen every 2 hours14
- Wear tightly woven, dark-colored clothing14
- Use wrap-around sunglasses blocking UVA and UVB rays14
Seasonal Sun Protection Strategies
UV protection is key all year. Check the UV Index regularly and act when it’s 3 or higher14. UVA rays go through windows and clouds, staying strong all year15.
Your skin’s health is in your hands – protect it wisely!
For babies under 6 months, skip sunscreen and use clothes and shade14. By following these tips, you can greatly lower your skin cancer risk16.
Early Detection Through Self-Examination
Protecting your skin starts with regular self-examinations. Mole screening is key to catching skin cancer early17. The Skin Cancer Foundation suggests doing a head-to-toe skin check once a month18.
Make your monthly self-examination thorough and systematic. Follow these steps for early detection:
- Use good lighting and a full-length mirror
- Check all areas of your body, including hard-to-see spots
- Document existing moles with photographs for comparison
- Look for the ABCDEs of melanoma17:
- Asymmetry: Irregular shape of moles
- Border: Uneven or ragged edges
- Color: Multiple colors or uneven pigmentation
- Diameter: Larger than a pencil eraser
- Evolving: Changes in size, shape, or color
Watch for spots that itch, bleed, or don’t heal in three weeks17. These could be signs needing medical attention18.
Only 9% to 18% of people do monthly skin self-exams19. By doing this regularly, you boost your chances of finding skin cancer early17.
Remember: Early detection can save lives.
When to Seek Professional Medical Evaluation
Keeping your skin healthy means getting medical help early. Knowing when to see a dermatologist is key to catching skin problems early20.
Emergency Warning Signs
Some skin changes need quick doctor visits. Look out for these urgent signs:
- Moles that change size, shape, or color fast
- Sores or wounds that won’t heal
- Skin lesions that bleed without reason
- Painful or sore skin growths
Scheduling Regular Skin Screenings
Getting regular mole checks is vital for your skin. Dermatologists suggest yearly skin exams for those at higher risk20. A full-body skin check usually takes about 10 minutes20.
At a dermatology check-up, doctors can:
- Use tools like dermatoscopes to look at skin layers20
- Spot suspicious spots that need more looking into
- Do biopsies if needed20
Spotting problems early can lead to better treatment results and fewer complications20. Your skin health is worth the proactive approach.
Remember, catching potential issues early can save lives and reduce treatment complexity.
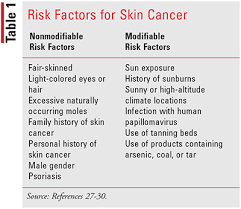
Risk Factors and Genetic Predisposition
Understanding your risk for skin cancer involves looking at both genetics and the environment. You can’t change your genes, but knowing your risk can help you take steps to prevent it21.
Genetics are a big part of who gets skin cancer. About 5% to 10% of melanomas are inherited, with some families at much higher risk22. Up to 10% of cancers come from inherited genetic changes21.
- People with certain genetic mutations might face a 60-90% chance of getting melanoma21
- CDKN2A mutations cause 22% of melanoma cases21
- Genetic changes can lead to cancer earlier, with some getting melanoma between 33-45 years old21
Physical traits can also show if you’re at higher risk. Those with red or blonde hair, blue or green eyes, and lighter skin are more likely to get skin cancer21. These traits often mean you’re more sensitive to UV rays.
Your family history is also key. If many relatives have had melanoma or related cancers, think about genetic counseling. Experts suggest it if you have three or more melanomas or a strong family history of cancer21.
Even with a genetic risk, prevention is still important. Protect your skin, watch for changes, and see doctors often to manage your risk.
Treatment Options and Success Rates
Skin cancer treatment has made big strides, offering hope to many. Every year, about 5.3 million new cases are found in the United States. Finding effective treatments is key23.
Dermatologists have many ways to treat skin cancer, based on the type and stage. The main methods are:
- Surgical Removal
- Radiation Therapy
- Immunotherapy
- Targeted Therapy
Mohs surgery is a standout, with a success rate of up to 99% for skin cancer24. It’s a precise surgery that removes cancer while keeping healthy skin.
| Treatment Method | Success Rate | Best Used For |
|---|---|---|
| Mohs Surgery | 99% | Precise removal of skin cancer |
| Immunotherapy | 70-80% | Advanced melanoma cases |
| Radiation Therapy | 85% | Non-surgical treatment options |
Only 1 to 2 out of 500 skin cancer cases are deadly23. There are twelve FDA-approved immunotherapy options for skin cancer. This gives patients many treatment choices23.
Your treatment will depend on the cancer type, stage, location, and your health. Early detection is the most important factor in treating skin cancer successfully.
Conclusion
Understanding skin cancer prevention is key to keeping you healthy. By being proactive, you can lower your risk of this serious disease. Using sunscreen with an SPF of 15 or higher can cut melanoma risk by 50%.
This makes sun protection very important25. Also, 86% of melanomas come from UV radiation25.
Skin cancer is a big health issue in the U.S., being the most common cancer26. Finding it early is crucial for treatment success. Regular self-checks and doctor visits are vital for your skin health.
People who get screened are 160% more likely to find in situ melanoma and 80% more likely to find stage 1 melanoma27.
Your effort in preventing skin cancer can really help. Stay safe by avoiding too much sun, wearing protective clothes, and getting skin checks often. While it might seem tough, knowing and being careful are your best tools for good skin health and catching problems early.
FAQ
What are the most common types of skin cancer?
There are three main types of skin cancer. Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC) is the most common and least aggressive. It usually appears on sun-exposed areas. Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC) can spread more quickly. Melanoma is the most dangerous form that can spread rapidly if not caught early.
How often should I perform a skin self-examination?
You should do a thorough skin self-examination once a month. This helps you get to know your skin better. It also helps you spot any new or changing moles, lesions, or unusual growths. Pay extra attention to sun-exposed areas and hard-to-see spots like your back, scalp, and between toes.
What does the ABCDE rule mean for mole detection?
The ABCDE rule is a key tool for spotting potentially cancerous moles:
– Asymmetry: One half doesn’t match the other
– Border: Irregular, ragged, or blurred edges
– Color: Multiple colors or uneven color distribution
– Diameter: Larger than 6mm (about the size of a pencil eraser)
– Evolving: Changes in size, shape, or color over time
Who is at highest risk for developing skin cancer?
People with fair skin, extensive sun exposure, and a history of sunburns are at higher risk. Those with a family history of skin cancer, weakened immune system, and many moles are also at risk. Light-haired, light-eyed, and easily sunburned individuals are especially vulnerable. However, anyone can get skin cancer, regardless of skin tone.
When should I see a dermatologist about a suspicious skin mark?
See a dermatologist if you notice:
– A new or changing mole
– A sore that doesn’t heal within 2-3 weeks
– A mole with irregular borders
– Growths that are asymmetrical or multicolored
– Any skin lesion that bleeds, itches, or causes discomfort
How can I protect myself from UV damage?
To protect yourself, use broad-spectrum sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher. Wear protective clothing and wide-brimmed hats. Seek shade during peak sun hours (10 AM – 4 PM). Avoid tanning beds. Reapply sunscreen every 2 hours when outdoors.
Are all skin cancers fatal?
No, most skin cancers are treatable if caught early. BCC and SCC have very high survival rates when treated promptly. Even melanoma, if detected early, has an excellent prognosis. This highlights the importance of regular screenings and self-examinations.
Source Links
- https://www.clearskin.in/blog/warning-signs-of-skin-cancer/ – 7 Warning Signs of Skin Cancer You Shouldn’t Ignore
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/skin-cancer/symptoms-causes/syc-20377605 – Skin cancer – Symptoms and causes
- https://www.skincancer.org/skin-cancer-information/ – Skin Cancer Information
- https://www.cancercenter.com/cancer-types/skin-cancer/symptoms – Skin Cancer Symptoms: ABCDE Signs and What It Looks Like
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/14391-melanoma – Melanoma: Symptoms, Staging & Treatment
- https://www.cancer.org/cancer/types/melanoma-skin-cancer/detection-diagnosis-staging/signs-and-symptoms.html – Signs of Melanoma Skin Cancer
- https://www.webmd.com/melanoma-skin-cancer/ss/skin-cancer-and-skin-lesions-overview – Precancerous Skin Lesions and Skin Cancer
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6275160/ – Malignant transformation of a non-healing traumatic wound on the lower extremity: A case report
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10312005/ – Skin immunity in wound healing and cancer
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41416-021-01309-w – Cancer metastasis as a non-healing wound – British Journal of Cancer
- https://www.cancer.gov/types/skin/moles-fact-sheet – Common Moles, Dysplastic Nevi, and Risk of Melanoma
- https://www.cancer.org/cancer/types/melanoma-skin-cancer/causes-risks-prevention/risk-factors.html – Melanoma Skin Cancer Risk Factors | Melanoma Risk Factors
- https://www.cancerresearchuk.org/about-cancer/skin-cancer/risks-causes – Risks and causes of skin cancer
- https://www.cdc.gov/skin-cancer/sun-safety/index.html – Sun Safety Facts
- https://www.skincancer.org/risk-factors/uv-radiation/ – UV Radiation
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/10985-ultraviolet-radiation – Ultraviolet (UV) Radiation: What It Is & Its Effect on Your Skin
- https://www.skincancer.org/early-detection/self-exams/ – Self-Exams
- https://www.cancer.org/cancer/risk-prevention/sun-and-uv/skin-exams.html – How to Do a Skin Self-Exam | Examine Your Skin
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC2440310/ – Melanoma Early Detection with Thorough Skin Self-Examination: The “Check It Out” Randomized Trial
- https://www.skincancer.org/early-detection/annual-exams/ – Annual Exams
- https://www.curemelanoma.org/blog/how-genetics-and-family-history-contribute-to-melanoma-risk – How Genetics and Family History Contribute to Melanoma Risk – Melanoma Research Alliance
- https://www.cancer.gov/types/skin/hp/skin-genetics-pdq – Genetics of Skin Cancer (PDQ®)
- https://www.cancerresearch.org/cancer-types/skin-cancer – Immunotherapy for Skin Cancer – Cancer Research Institute
- https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/surgery-for-skin-cancer – Surgery for Skin Cancer
- https://www.skincancer.org/media-and-press/skin-cancer-issues-and-research/ – Skin Cancer Issues and Research
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK441949/ – Skin Cancer – StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf
- https://www.cancer.gov/news-events/cancer-currents-blog/2022/skin-cancer-screening-melanoma-overdiagnosis – Study Adds to Debate about Melanoma Screening