Introduction
Isotretinoin, often known by its former brand name Accutane, is a powerful retinoid medication primarily used to treat severe acne. Its efficacy and transformative results have made it a cornerstone in dermatology, especially for patients whose acne has not responded to other treatments.
Mechanism of Action
Isotretinoin works by addressing several key factors that contribute to acne formation:
- Reduces Sebum Production: It shrinks the sebaceous glands, significantly reducing the amount of oil (sebum) produced. This decrease in sebum helps to prevent the clogging of pores, a primary cause of acne.
- Prevents Clogging of Pores: By normalizing the shedding of dead skin cells within hair follicles, it reduces the formation of comedones (blackheads and whiteheads).
- Anti-Inflammatory Properties: It has anti-inflammatory effects that help reduce the redness and swelling associated with severe acne.
- Reduces Bacterial Growth: By lowering sebum production, isotretinoin reduces the growth environment for Propionibacterium acnes (P. acnes), the bacteria involved in acne development.
- Influences Cell Differentiation: It promotes the normalization of keratinization, preventing the formation of microcomedones which can develop into acne lesions.
When To Use
Isotretinoin, widely known under its former brand name Accutane, is a potent retinoid medication primarily used to treat severe acne. Due to its effectiveness, it has been used for various other dermatological conditions as well. Below is an in-depth exploration of its uses:
1. Severe Acne
Primary Use: Isotretinoin is primarily prescribed for severe nodular or cystic acne that has not responded to other treatments, such as topical treatments and antibiotics.
Mechanism:
- Sebum Reduction: It significantly reduces sebum (oil) production by shrinking the sebaceous glands, which helps prevent the clogging of pores.
- Anti-inflammatory: It has anti-inflammatory properties that reduce redness and swelling.
- Comedolytic: It prevents the formation of comedones (blackheads and whiteheads) by normalizing the shedding of dead skin cells within the hair follicles.
- Antibacterial: By reducing sebum, isotretinoin decreases the proliferation of Propionibacterium acnes (P. acnes), the bacteria involved in acne development.
Dosage: Typically taken as an oral capsule, the dosage is usually based on body weight, with a cumulative dose aimed at 120-150 mg/kg over a 15-20 week period.
Effectiveness: Many patients experience long-term remission of acne after one course of treatment, making it highly effective for severe cases.
2. Moderate Acne
Use: In cases where moderate acne is resistant to other treatments, this drug may be prescribed as an alternative.
Mechanism and Dosage: Similar to its use in severe acne, but often at lower doses and shorter treatment durations to minimize side effects.
3. Rosacea
Use: Isotretinoin is sometimes used off-label for severe cases of rosacea, particularly when patients do not respond to standard therapies like antibiotics and topical treatments.
Mechanism: The drug helps by reducing sebaceous gland activity and inflammation, which are significant contributors to rosacea symptoms.
4. Hidradenitis Suppurativa
Use: This chronic skin condition characterized by painful lumps under the skin, particularly in the armpits and groin, can be treated with isotretinoin in severe cases.
Mechanism: It reduces the size and activity of sebaceous glands, which can help prevent the formation of painful nodules and abscesses.
5. Severe Seborrheic Dermatitis
Use: For patients with severe seborrheic dermatitis unresponsive to other treatments, isotretinoin can be an effective option.
Mechanism: The reduction in sebum production helps manage the excessive oiliness and inflammation associated with seborrheic dermatitis.
6. Prevention of Skin Cancer
Use: Isotretinoin has been used as a chemopreventive agent in patients at high risk for skin cancers, such as squamous cell carcinoma, especially in those with a history of multiple nonmelanoma skin cancers.
Mechanism: It induces cell differentiation and apoptosis in pre-cancerous cells, reducing the risk of progression to cancer.
7. Neuroblastoma
Use: In pediatric oncology, isotretinoin is used as part of the treatment regimen for high-risk neuroblastoma, a type of cancer that forms in certain types of nerve tissue.
Mechanism: It promotes the differentiation of neuroblastoma cells, making them less likely to proliferate.
Adverse effects
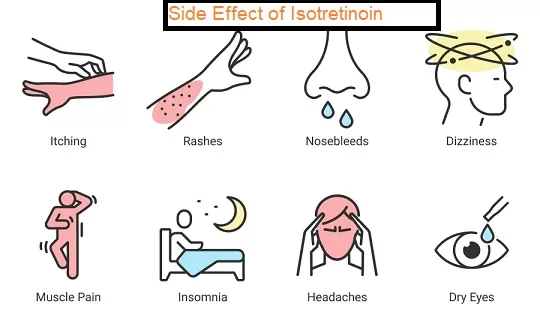
Common Side Effects:
- Dry Skin and Lips: The most common side effect, often leading to cracked lips and dry patches of skin.
- Dry Eyes and Nose: May cause irritation, redness, and nosebleeds.
- Skin Sensitivity: Increased sensitivity to the sun, requiring diligent use of sunscreen.
- Initial Acne Flare-Up: Acne may worsen temporarily at the start of treatment.
- Thinning Hair: Some users report hair loss or thinning during treatment.
- Muscle and Joint Pain: Particularly in younger users and those engaging in vigorous physical activity.
- Headaches: Common but usually mild.
Less Common Side Effects:
- Rash: Sometimes severe and requiring medical attention.
- Nausea or Vomiting: Gastrointestinal disturbances.
- Changes in Mood: Such as depression or anxiety.
- Changes in Blood Sugar Levels: Affecting diabetic patients primarily.
- Elevated Liver Enzymes: Indicating stress on the liver, requiring monitoring.
Serious Side Effects:
- Severe Mood Changes: Including depression, suicidal thoughts, or aggressive behavior.
- Vision Problems: Including blurred vision or decreased night vision.
- Hearing Issues: Such as tinnitus or decreased hearing ability.
- Severe Stomach Pain: Possible pancreatitis.
- Severe Skin Reactions: Including Stevens-Johnson syndrome, a rare but life-threatening condition.
- Bone and Joint Problems: Long-term use can affect bone density.
- Liver Damage: Indicated by jaundice (yellowing of the skin or eyes), necessitating immediate medical attention.
- Intracranial Hypertension: Increased pressure within the skull, presenting as severe headaches, vision changes, and dizziness.
Precautions:
- Pregnancy: Isotretinoin teratogenicity effect cause severe birth defects. Women of childbearing age must use two forms of contraception and undergo regular pregnancy tests.
- Regular Monitoring: Blood tests are often required to monitor liver function, lipid levels, and other health indicators.
- Mental Health: Patients should be monitored for signs of depression or other mood changes.
Recommendations:
- Moisturizers and Lip Balms: To manage dryness.
- Sunscreen: To protect against sunburn due to increased sensitivity.
- Hydration: Drinking plenty of water to help alleviate dryness.
- Avoiding Waxing: To prevent skin damage while on the medication.
How Long after Taking Isotretinoin Can I Drink Alcohol ?
After completing a course of isotretinoin, it is generally advised to wait until the medication is fully cleared from your system before consuming alcohol. Isotretinoin has a half-life of approximately 10-20 hours, but it can take longer for its metabolites to be completely eliminated. Given this, it is prudent to wait at least several days to a couple of weeks after your last dose before consuming alcohol. This timeframe allows your liver and body to recover from the potential strain of the medication and reduces the risk of adverse effects.
Best Isotretinoin Products on the Market
Systemic Isotretinoin Products (Oral)
-
Accutane (Isotretinoin)
- Description: The original brand of isotretinoin, highly effective but discontinued in the U.S. However, it set the standard for generic formulations.
-
Claravis
- Description: A popular generic version of isotretinoin, known for its efficacy in treating severe acne.
-
Amnesteem
- Description: Another well-known generic isotretinoin, available in various dosages to cater to different patient needs.
-
Absorica
- Description: A unique isotretinoin formulation that is better absorbed with or without food, offering flexibility for patients.
-
Myorisan
- Description: A commonly prescribed generic isotretinoin, effective for severe recalcitrant nodular acne.
Topical Retinoid Alternatives (Less potent but useful for mild to moderate acne)
-
Differin Gel (Adapalene 0.1%)
- Description: Available over-the-counter, Differin is a topical retinoid that is effective for treating mild to moderate acne. It’s less potent than oral isotretinoin but a good option for less severe cases.
-
Tazorac (Tazarotene)
- Description: A topical retinoid available by prescription, effective for acne and psoriasis. It’s stronger than over-the-counter options but not as potent as systemic isotretinoin.
-
Retin-A (Tretinoin)
- Description: A prescription topical retinoid used to treat acne and reduce signs of aging. It’s effective but can cause irritation in some users.
Conclusion
Isotretinoin stands out as a highly effective treatment for severe and treatment-resistant acne. Its multi-faceted mechanism of action addresses the root causes of acne, leading to long-term remission for many patients. While systemic isotretinoin is the gold standard for severe cases, topical retinoid alternatives like Differin, Tazorac, and Retin-A offer solutions for less severe conditions.
If you’re considering isotretinoin, it’s crucial to consult with a dermatologist to discuss potential benefits, side effects, and the rigorous monitoring required during treatment. With the right guidance, it can be a game-changer for those struggling with severe acne.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) :
What is isotretinoin used for?
Isotretinoin is primarily used to treat severe nodular acne that has not responded to other treatments, including antibiotics. It works by reducing the amount of oil released by oil glands in your skin, helping your skin renew itself more quickly.
How does isotretinoin work?
Isotretinoin decreases the size and output of sebaceous (oil) glands, reduces bacterial growth on the skin, prevents clogged pores, and has anti-inflammatory properties. This multifaceted approach helps to clear severe acne effectively.
What are the common side effects of isotretinoin?
Common side effects include: Dry skin and lips Dry eyes and nose Skin sensitivity Initial acne flare-up Thinning hair Muscle and joint pain Headaches
What are the serious side effects of isotretinoin?
Serious side effects can include: Severe mood changes, including depression and suicidal thoughts Vision problems Hearing issues Severe stomach pain or pancreatitis Severe skin reactions Liver damage Intracranial hypertension
How long does it take for isotretinoin to work?
Most patients begin to see improvement within 1-2 months of starting treatment, but it can take up to 4-6 months to see the full effects. Acne may worsen initially before it starts to improve.
Can I drink alcohol while taking isotretinoin?
It is generally advised to avoid alcohol while taking isotretinoin due to the increased risk of liver damage and elevated triglycerides. If you choose to drink, it should be in moderation and discussed with your healthcare provider.
Why do I need to avoid pregnancy while taking isotretinoin?
Isotretinoin is highly teratogenic, meaning it can cause severe birth defects. Women of childbearing age must use two forms of contraception and undergo regular pregnancy tests before, during, and after treatment.
How long should I wait after finishing isotretinoin before becoming pregnant?
It is recommended to wait at least one month after completing isotretinoin treatment before trying to become pregnant to ensure the drug has fully cleared from your system.
What kind of monitoring is required while on isotretinoin?
Regular monitoring is essential, including: Blood tests to check liver function and lipid levels Pregnancy tests for women of childbearing age Follow-up appointments with your healthcare provider to monitor side effects and progress
Can I use other acne treatments while on isotretinoin?
Generally, you should avoid using other acne treatments, especially topical ones that can be irritating, such as retinoids and benzoyl peroxide. Your dermatologist will guide you on what is safe to use alongside isotretinoin.
What should I do if I miss a dose?
If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember on the same day. If it's almost time for your next dose, skip the missed dose and resume your regular dosing schedule. Do not double up doses.
Foods to avoid while on isotretinoin
While taking isotretinoin , certain foods or beverages should be limit or avoid such as alcohol, high fat foods, vitamin A rich foods and supplements , sugary foods, dietary products, processed and fast food.