Introduction
Anxiety is a normal and often healthy emotion. However, when a person feels disproportionate levels of anxiety, it can become a mental health disorder. It is the most common mental illness in the United States, affecting 40 million adults age 18 and older, or 18.1% of the population every year. Stress can be debilitating and affect various aspects of life, including work, relationships, and overall well-being. Understanding the causes, recognizing the signs and symptoms, seeking appropriate treatment, and taking necessary precautions are essential in managing effectively.
Causes of Anxiety;
The exact causes of anxiety disorders are unknown, but there are a number of factors that may contribute to their development, including:
- Biological Factors:
- Genetics: A family history can increase the likelihood of experiencing anxiety.
- Brain Chemistry: Imbalances in neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine can contribute to it.
- Psychological Factors:
- Stress: High levels of stress from work, relationships, or life events can exacerbate the symptom.
- Trauma: Past traumatic experiences can lead to conditions like PTSD (Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder).
- Personality Traits: Certain personality traits, such as perfectionism or a tendency to worry excessively, can have a triggering effect .
- Environmental Factors:
- Childhood Environment: Adverse childhood experiences, including neglect or abuse, can contribute to anxiety disorders.
- Substance Abuse: Alcohol, drugs, or other substances, can worsen or trigger symptoms.
- Living Conditions: Living in a high-crime area or in constant instability can lead to chronic anxiety.
- Medical Factors:
- Chronic Illness: Dealing with a long-term medical condition can cause anxiety.
- Medications: Some medications may have anxiety as a side effect.
- Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations, like those during menopause, can lead to symptoms.
- Neurological Factors:
- Neurological Disorders: Conditions like epilepsy or multiple sclerosis can be associated with anxiety.
- Imbalance in the Autonomic Nervous System: Dysregulation of the fight-or-flight response can contribute to this disorders.
- Social Factors:
- Social Isolation: Loneliness and lack of social support can increase the risk of anxiety.
- Peer Pressure: Negative social interactions or pressures from peers can lead to anxiety in some individuals.
- Cognitive Factors:
- Negative Thinking Patterns: Habitual negative thinking, such as catastrophizing or overgeneralizing, are one of the factor.
- Worrying About the Future: Excessive worry about what might happen in the future can lead to generalized anxiety disorder (GAD).
- Financial Factors:
- Financial Stress: Struggling with debt, job insecurity, or financial instability .
- Economic Factors: Economic downturns and recessions can contribute to heightened anxiety levels in populations.
- Relationship Factors:
- Conflict: Frequent conflict or unhealthy dynamics in relationships can lead to anxiety.
- Attachment Issues: Insecure attachment styles developed in childhood can affect adult relationships and cause anxiety.
- Life Transitions:
- Major Life Changes: Events like moving, divorce, starting a new job, or retirement can trigger anxiety.
- Transitions in Developmental Stages: Adolescence, midlife, and aging can be associated with unique anxieties.
Seeking help from mental health professionals can provide support and treatment options for managing anxiety.
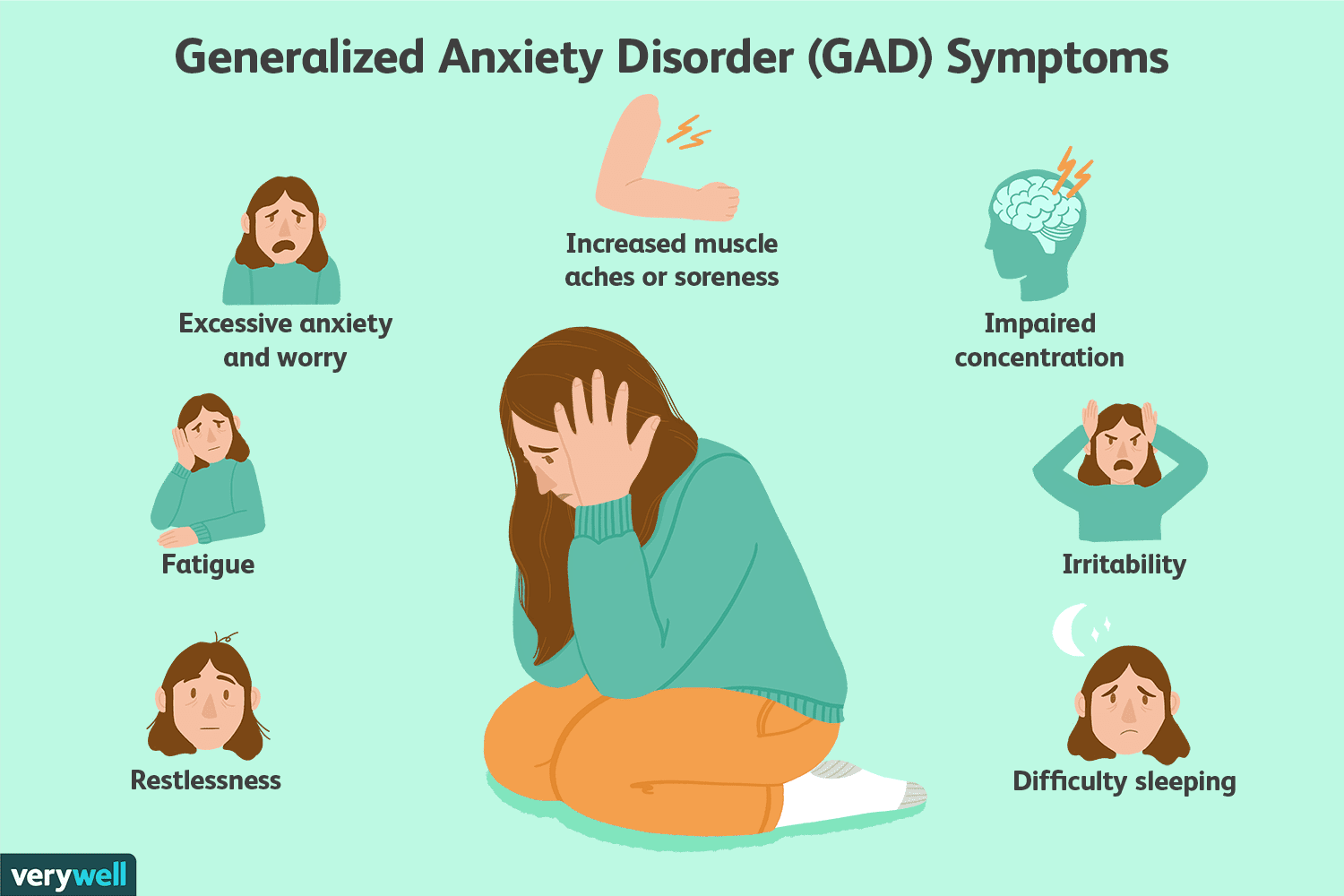
Symptoms ;
- Irritability or feeling on edge.
- Fatigue and disturbed sleep patterns.
- Muscle tension and physical discomfort.
- Panic attacks or sudden surges of fear.

- difficult concentrating or thinking clearly.
- avoidance of situation.
- change in appetite and sleep problem
Management;
It’s important to note that anxiety management is a highly individualized process, and what works for one person may not work for another. Here are some common approaches to manage it:
- Professional Help:
- Therapy: Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), exposure therapy, and other forms of psychotherapy can help individuals learn to cope with it.
- Medication: In some cases, medication prescribed by a psychiatrist, such as antidepressants or anxiolytic medications, may be necessary to alleviate severe symptoms.
- Consultation: Consulting with a mental health professional can help determine the most appropriate treatment plan for your specific type and level of anxiety.
- Lifestyle Changes:
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity can reduce stress and anxiety by releasing endorphins, which are natural mood lifters.
- Healthy Diet: A balanced diet can help regulate mood and energy levels. Avoid excessive caffeine and alcohol.
- Adequate Sleep: Ensure you get enough quality sleep, as sleep deprivation can worsen symptoms.
- Limit Stressors: Identify and address sources of stress in your life, and try to reduce or eliminate them when possible.
- Stress Management Techniques:
- Deep Breathing: Practice deep breathing exercises to calm the nervous system. Techniques like diaphragmatic breathing or the 4-7-8 technique can be helpful.
- Progressive Muscle Relaxation: Learn to relax your body by systematically tensing and then releasing different muscle groups.
- Mindfulness and Meditation : These practices can help you stay present and reduce ruminative thoughts that often fuel anxiety.
- Yoga and Tai Chi: These mind-body practices integrate physical postures, breathing exercises, and meditation.
- Social Support:
- Talk to Friends and Family: Sharing your feelings with trusted loved ones can provide emotional support and reduce feelings of isolation.
- Support Groups: Consider joining a support group for individuals dealing with similar issues.
- Time Management:
- Organize and Prioritize: Create daily or weekly schedules to manage your time effectively and reduce the feeling of being overwhelmed.
- Set Realistic Goals: Divide tasks into manageable steps and establish attainable goals.
- Avoid Triggers:
- Identify Triggers: Recognize situations, places, or people that trigger your symptoms and try to minimize exposure.
- Limit News and Social Media: Constant exposure to negative news or social media can have detrimental effects . Consider taking breaks from such sources.
- Self-Care:
- Hobbies and Interests: Engage in activities you enjoy and that provide relaxation and a sense of accomplishment.
- Self-Compassion: Be kind to yourself and practice self-compassion. Avoid self-criticism and perfectionism.
- Seek Professional Advice:
- If your anxiety is significantly affecting your daily life, don’t hesitate to seek help from a mental health professional. They can provide tailored guidance and treatment options.
Remember that managing anxiety is an ongoing process, and it may require time and effort to find the strategies and techniques that work best for you. It’s important to be patient with yourself and seek support when needed
Precautions for Anxiety
There are a number of things that people can help themselves by taking precautions, including:
- Get enough sleep: Adequate sleep can contribute to the reduction of stress levels.
- Exercise regularly: Exercise is a great way to reduce stress and improve overall mood.
- Eat a healthy diet: Eating a healthy diet can help to improve overall health and well-being.
- Avoid caffeine and alcohol: Caffeine and alcohol can worsen symptoms.
- Learn relaxation techniques: Relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing and meditation, can help to reduce symptoms.
- Seek professional help: If significant distress, it is important to seek professional help.
Remember, anxiety is a treatable condition, and seeking support from friends, family, or mental health professionals can make a significant difference in overcoming it. By recognizing the causes, symptoms, and available treatment options, along with taking necessary precautions, individuals can regain control over their lives and find effective ways to cope with it. Always remember that you are not alone, and seeking help is a sign of strength, not weakness.
Frequently Asked Questions ( FAQs );
What is anxiety?
Anxiety is a normal emotional response to stressful situations. However, when anxiety becomes excessive, persistent, and interferes with daily life, it can be classified as an anxiety disorder.
What are the symptoms of anxiety?
Symptoms can vary but may include: Excessive worry and fear. Physical symptoms like racing heart, sweating, difficulty breathing, muscle tension, and headaches. Difficulty concentrating and sleeping. Panic attacks. Avoidance of situations that trigger anxiety.
What causes anxiety?
The exact cause is unknown, but it likely involves a combination of factors, including genetics, brain chemistry, life experiences, and personal vulnerability.
Is anxiety a personal weakness?
Absolutely not! Anxiety is a common mental health condition, not a character flaw.
How is anxiety diagnosed?
A mental health professional, like a psychiatrist or therapist, will typically diagnose anxiety based on a clinical assessment, including your symptoms, medical history, and psychological evaluation.
What are the treatment options for anxiety?
Several effective treatments are available, including therapy (e.g., cognitive-behavioral therapy), medication (anti-anxiety medications), and lifestyle changes (e.g., exercise, relaxation techniques, mindfulness). Often, a combination of these approaches works best.
How long does it take to treat anxiety?
Treatment times vary depending on the severity of the anxiety and individual response. Some people see improvement within weeks, while others may require longer-term treatment.
Can I manage anxiety on my own?
While self-help strategies can be helpful, professional treatment is crucial for effectively managing anxiety.
What can I do to help myself feel better?
Several things can help, including: Engaging in regular physical activity. Practicing relaxation techniques (e.g., yoga, meditation, deep breathing exercises). Reducing stress and caffeine intake. Getting enough sleep. Challenging negative thoughts and catastrophizing. Connecting with supportive friends and family. Joining a support group.
Where can I find help and support?
Many resources are available, including: Your doctor or a mental health professional. National anxiety hotlines (e.g., Anxiety and Depression Association of America (ADAA): 1-800-950-NAMI (6264)). Mental health organizations (e.g., Anxiety and Depression Association of America (ADAA)). Online support groups and forums.